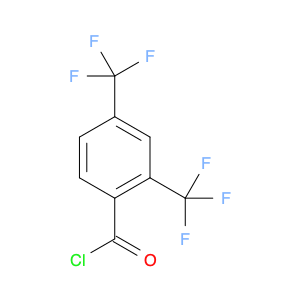
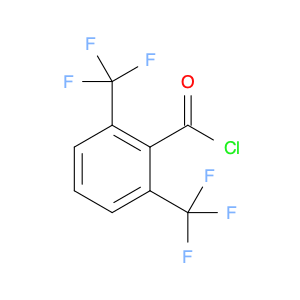
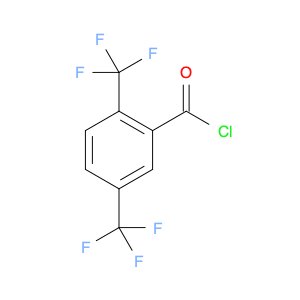
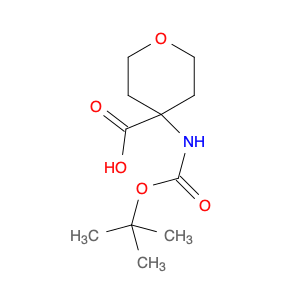
2,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl chloride, also known as BTFNBC, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This compound plays a crucial role as an acylating agent in various reactions, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. Its unique properties make it a valuable tool for modifying organic molecules and creating new compounds with enhanced properties.In chemical synthesis, 2,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl chloride acts as a reactive intermediate in the acylation of various functional groups. It is commonly used to introduce the trifluoromethylbenzoyl group into organic molecules, which can significantly alter their physicochemical properties. This acyl chloride can selectively react with nucleophiles like amines, alcohols, and thiols to form amides, esters, and thioesters, respectively. The presence of the trifluoromethyl groups enhances the stability and lipophilicity of the resulting compounds, making them useful in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.Furthermore, 2,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl chloride can also participate in various cross-coupling reactions, such as the Suzuki-Miyaura and Heck coupling, to form biaryl compounds with high regioselectivity. These biaryl derivatives are essential building blocks in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, natural products, and functional materials. Overall, the application of BTFNBC in chemical synthesis offers chemists a powerful tool to tailor the properties of molecules for specific applications.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com