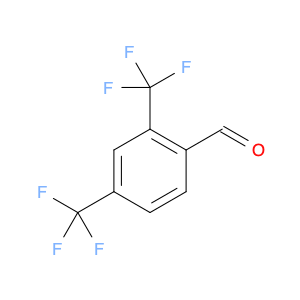
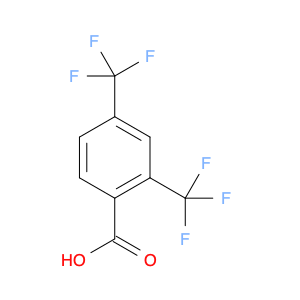
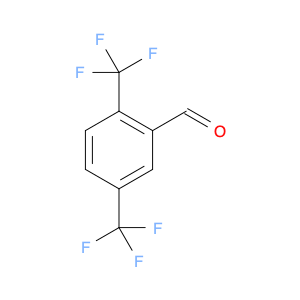
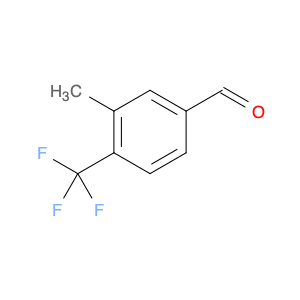
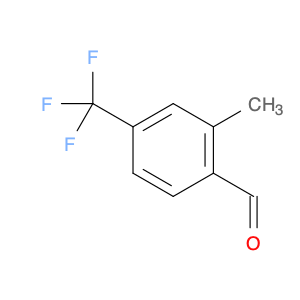
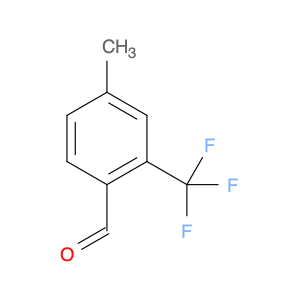
2,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde, also known as BTB, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This compound plays a crucial role in various organic reactions due to its unique chemical properties. One of the key applications of 2,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde is its use as a building block in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials with specific properties.In organic synthesis, 2,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde serves as a valuable precursor for the preparation of various functionalized molecules. Its trifluoromethyl groups can be selectively modified to introduce specific functionalities, making it a powerful tool for the construction of complex organic structures. Additionally, the aldehyde group in BTB enables easy manipulation through a variety of chemical transformations, allowing for further diversification of the final product.Furthermore, 2,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde is renowned for its ability to participate in diverse reactions such as condensations, reductions, and nucleophilic additions. These versatile reactivity patterns make BTB a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of heterocycles, natural products, and fine chemicals. Its unique electron-deficient aromatic core also imparts desirable electronic properties to the final compounds, enhancing their potential applications in various fields.Overall, the strategic application of 2,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde in chemical synthesis offers a wide array of possibilities for the creation of novel molecules with tailored functionalities and properties. Its versatility, reactivity, and compatibility with different synthetic routes make it an indispensable building block for the design and development of innovative compounds in the realm of organic chemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com