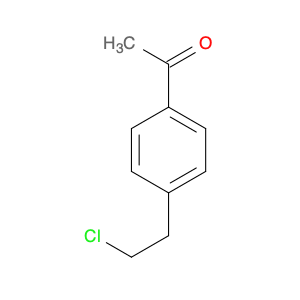
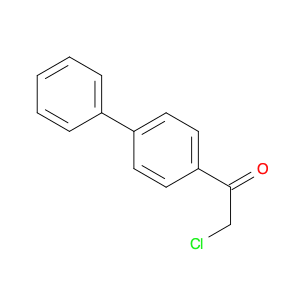
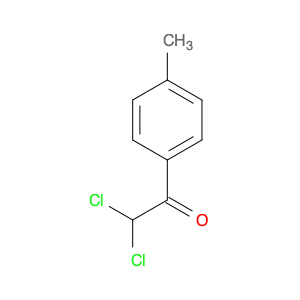
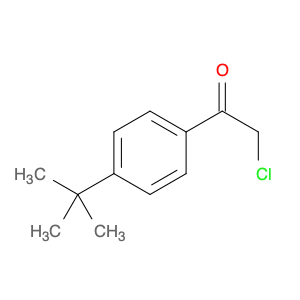
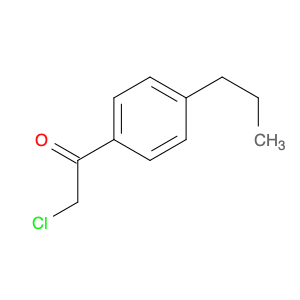
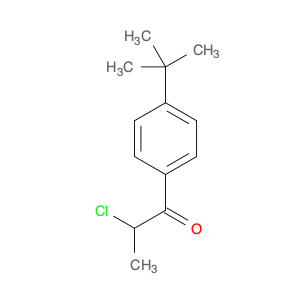
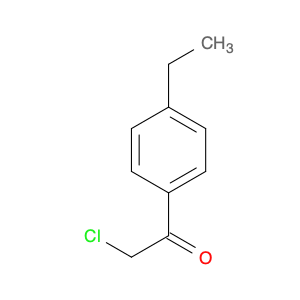
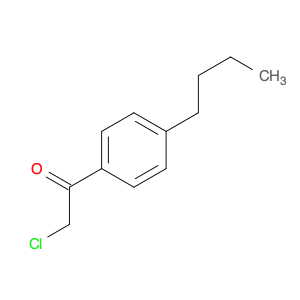
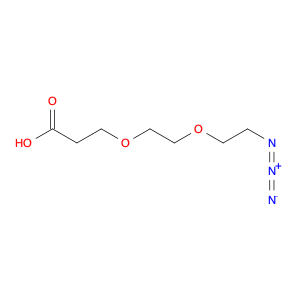
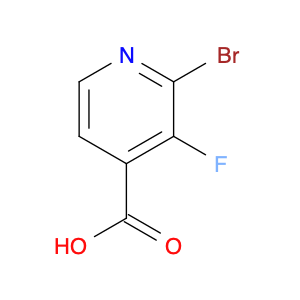
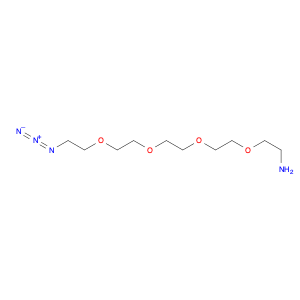
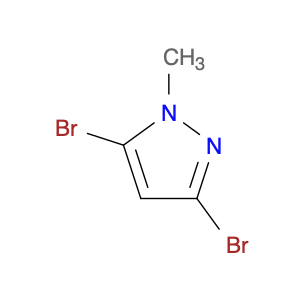
1-(4-(2-Chloroethyl)phenyl)ethanone, also known as $name$, serves as a key intermediate in chemical synthesis processes. This compound plays a crucial role in organic chemistry due to its unique structural properties and versatile reactivity. In particular, $name$ is commonly employed in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals.$name$ is used as a building block in the production of complex organic molecules, where its phenyl and ethanone moieties enable the introduction of functional groups through synthetic manipulations such as acylation, alkylation, and condensation reactions. The 2-chloroethyl group in $name$ provides a reactive site for nucleophilic substitution reactions, allowing for the selective modification of the molecule to generate diverse chemical entities.Furthermore, the presence of the chloroethyl group in $name$ imparts unique properties to the final products, making it a valuable precursor for the synthesis of bioactive compounds and advanced materials. By judiciously incorporating $name$ into synthetic pathways, chemists can access a wide range of structurally diverse compounds with tailored properties for various applications in the fields of pharmaceuticals, materials science, and agrochemicals.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com