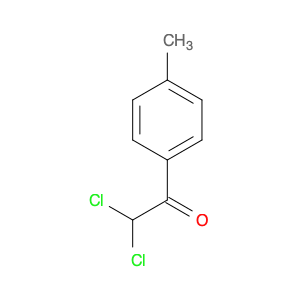
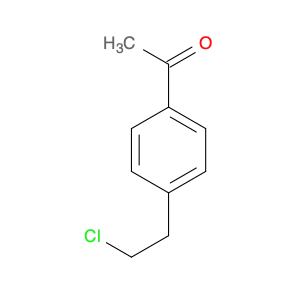
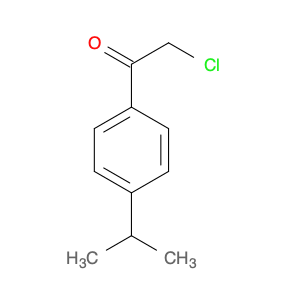
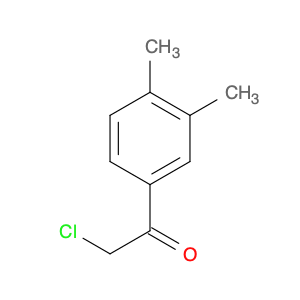
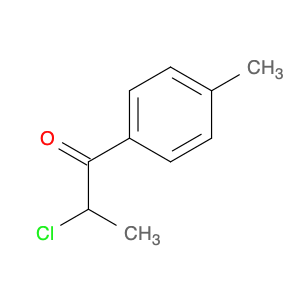
2,2-Dichloro-1-(p-tolyl)ethanone, also known as (p-Chlorophenyl)-2,2-dichloroethyl ketone, is a key intermediate widely used in chemical synthesis processes. Due to its unique chemical properties, this compound plays a crucial role in the production of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals.In chemical synthesis, 2,2-Dichloro-1-(p-tolyl)ethanone serves as a versatile building block for the creation of complex molecules. It can undergo different types of reactions such as nucleophilic substitution, acylation, and condensation, enabling the formation of diverse chemical structures. This compound is particularly valued for its ability to introduce the dichloroethyl and p-tolyl groups into target molecules, thereby altering their physicochemical properties and biological activities.Moreover, 2,2-Dichloro-1-(p-tolyl)ethanone is commonly employed in the synthesis of chiral compounds and heterocycles, where its unique structure and reactivity facilitate the construction of stereochemically complex molecules with high selectivity. By incorporating this intermediate into various synthetic pathways, chemists can achieve precise control over the stereochemistry and functional group patterns of the final products, making it a valuable tool in modern organic synthesis.Overall, the application of 2,2-Dichloro-1-(p-tolyl)ethanone in chemical synthesis underscores its significance as a strategic building block for the preparation of diverse organic compounds with tailored properties and functionalities.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com