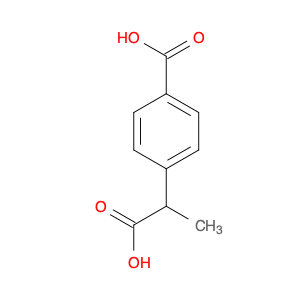
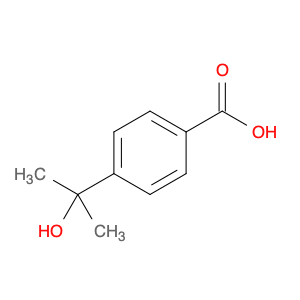
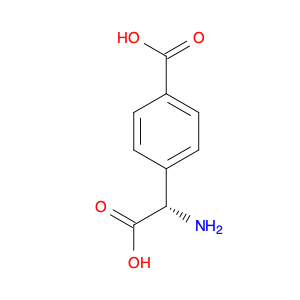
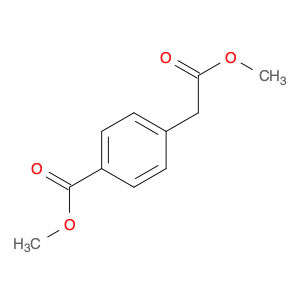
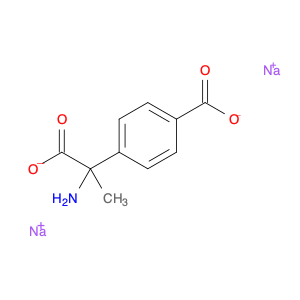
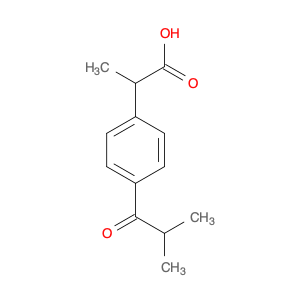
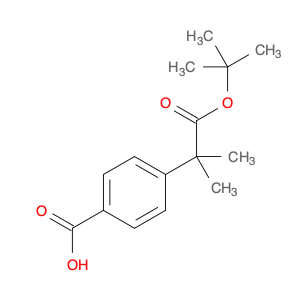
4-(1-Carboxyethyl)benzoic acid, also known as 4-(1-CEB), is a versatile compound commonly used in chemical synthesis applications. Its unique structure and functional groups make it an important building block for the preparation of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. In chemical synthesis, 4-(1-CEB) serves as a crucial intermediate in the production of a wide range of organic compounds. Its carboxylic acid group can undergo a variety of reactions, including esterification, amidation, and decarboxylation, to introduce different functional groups into the molecule. This flexibility allows chemists to tailor the properties of the final product according to the desired application.One of the key applications of 4-(1-CEB) in chemical synthesis is in the pharmaceutical industry, where it is used as a building block for the synthesis of drug candidates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). By incorporating 4-(1-CEB) into the molecular structure of pharmaceutical compounds, researchers can modulate the compound's pharmacokinetic properties, bioavailability, and therapeutic effects.Additionally, 4-(1-CEB) is also employed in the synthesis of specialty chemicals, such as fragrances, dyes, and advanced materials. Its ability to participate in diverse chemical reactions makes it a valuable tool for creating complex organic molecules with desired functionalities.Overall, the application of 4-(1-Carboxyethyl)benzoic acid in chemical synthesis highlights its importance as a versatile precursor for the preparation of a wide range of organic compounds with diverse applications.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com