Login |
Create New Account
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com
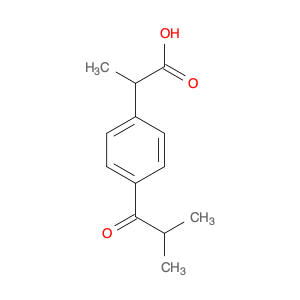
(2RS)-2-(4-ISOBUTYRYLPHENYL)PROPANOIC ACID
Catalog#: AR00FBG8 | CAS#: 65813-55-0 | MDL#: MFCD08275584 | MF: C13H16O3 | MW: 220.2643
| Packsize | Purity | Price | Availability | Quantity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg | $47.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 100mg | $75.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 250mg | $118.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 1g | $374.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 5g | $1,310.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart |
- Description
- Application
- Related Products
- Featured Products
| Catalog Number | AR00FBG8 |
| Chemical Name | (2RS)-2-(4-ISOBUTYRYLPHENYL)PROPANOIC ACID |
| CAS Number | 65813-55-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H16O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 220.2643 |
| MDL Number | MFCD08275584 |
| SMILES | CC(c1ccc(cc1)C(=O)C(C)C)C(=O)O |