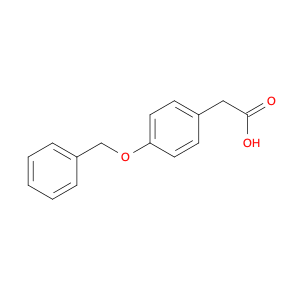
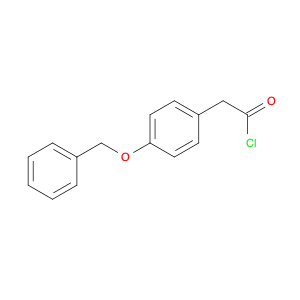
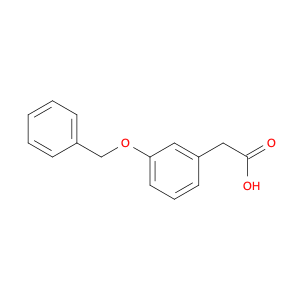
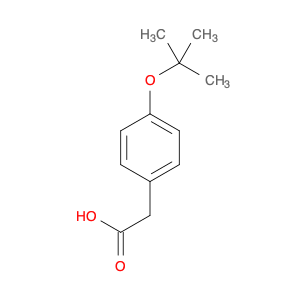
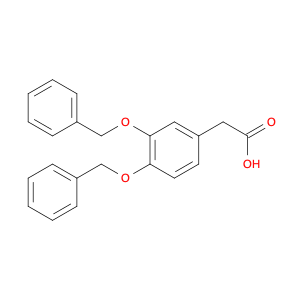
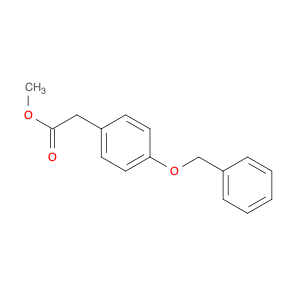
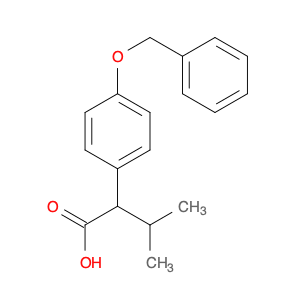
The chemical 2-(4-(Benzyloxy)phenyl)acetic acid, also known as $name$, serves as a versatile building block in chemical synthesis. This compound is commonly utilized as a key intermediate in the preparation of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials. Its unique chemical structure enables it to participate in a wide range of organic reactions, making it valuable for the synthesis of complex molecules.$name$ can be employed in the formation of esters, amides, and other functional derivatives through conventional chemical transformations such as esterification, amidation, and hydrogenation. Additionally, its aromatic benzyl group provides opportunities for further modification, allowing for the introduction of different substituents or functional groups to fine-tune the properties of the final product. In the context of medicinal chemistry, $name$ can be crucial for the synthesis of drug candidates or pharmacophores due to its ability to introduce specific structural motifs or pharmacophoric elements. Its presence in the molecular structure can influence the biological activity, pharmacokinetics, and target interactions of the final compound, making it a valuable tool in drug discovery and development efforts.Moreover, $name$ can serve as a starting material for the synthesis of polymeric materials, dyes, and other specialty chemicals. Its versatile reactivity and compatibility with various synthetic methodologies make it an attractive choice for designing and constructing complex molecular architectures. Whether in academic research or industrial applications, the use of $name$ in chemical synthesis promises to open up new avenues for innovation and discovery in the field of organic chemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com