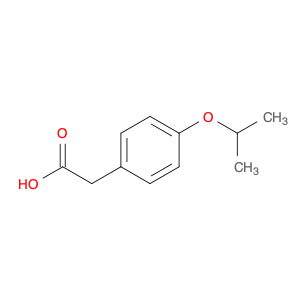
2-(4-Isopropoxyphenyl)acetic acid, also known as IPA, is a versatile compound commonly used in chemical synthesis. Due to its unique structure and properties, IPA is widely employed as a building block in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals.One of the key applications of IPA in chemical synthesis is its role as a starting material for the preparation of pharmaceutical intermediates. By incorporating IPA into different reaction sequences, chemists can manipulate its structure to produce diverse bioactive compounds with potential therapeutic applications. Additionally, the presence of the isopropoxy group in IPA allows for selective functionalization, enabling the precise modification of the molecule to enhance its biological activity or pharmacokinetic properties.Furthermore, IPA is frequently utilized in the synthesis of fragrance ingredients and dyes. Its aromatic phenyl ring provides a platform for creating complex aromatic compounds, while the isopropoxy group offers steric hindrance that can influence the molecule's reactivity and behavior in chemical processes. These features make IPA a valuable building block for developing novel fragrances, dyes, and other specialty chemicals with specific sensory or color properties.Overall, 2-(4-Isopropoxyphenyl)acetic acid plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis by serving as a versatile precursor for the preparation of a wide range of functional molecules. Its structural characteristics and reactivity make it an essential component in the toolkit of synthetic chemists working in various industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com