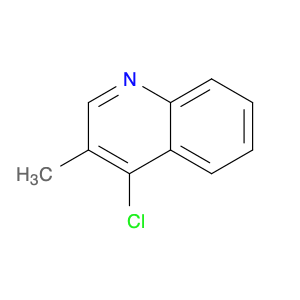
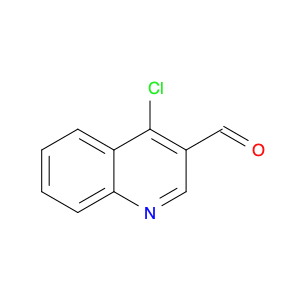
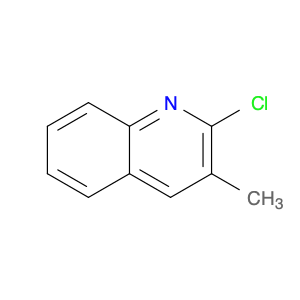
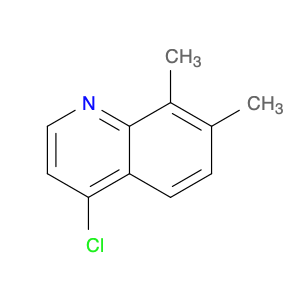
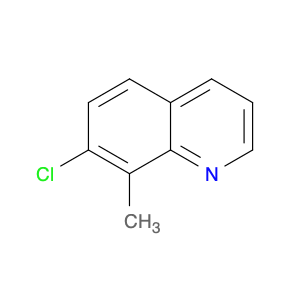
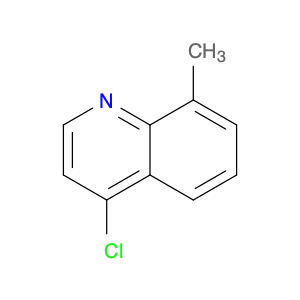
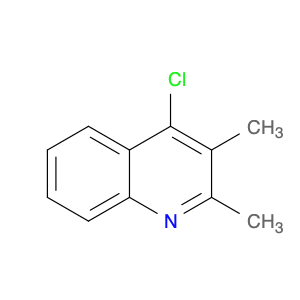
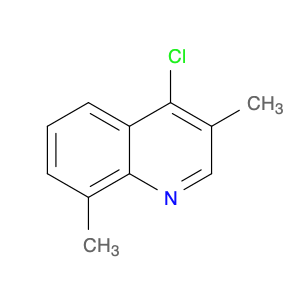
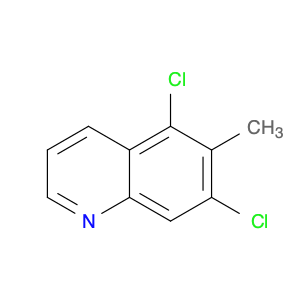
4-Chloro-3-methylquinoline, also known as $name$, is a versatile chemical compound widely used in various chemical synthesis processes. This compound serves as a valuable building block in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its unique structure and reactivity make it a key intermediate in the synthesis of diverse organic compounds.One significant application of 4-Chloro-3-methylquinoline is in the pharmaceutical industry. It is commonly utilized as a precursor in the synthesis of bioactive compounds and drug molecules. By incorporating this compound into the molecular structure of pharmaceuticals, researchers can modulate the compound's biological activity, improving its efficacy and specificity. Additionally, 4-Chloro-3-methylquinoline can act as a pharmacophore, influencing the compound's target-binding properties.In the field of agrochemicals, 4-Chloro-3-methylquinoline plays a crucial role in the development of pesticides and herbicides. By functionalizing this compound with specific groups, chemists can create potent agricultural chemicals with enhanced pesticidal or herbicidal activities. The versatility of 4-Chloro-3-methylquinoline allows for the synthesis of a wide range of agrochemical products tailored to target specific pests or weeds.Furthermore, in specialty chemical synthesis, 4-Chloro-3-methylquinoline can be employed to create novel compounds with unique properties. The presence of the chloro and methyl substituents on the quinoline ring provides opportunities for further functionalization, enabling the synthesis of custom-designed molecules for various applications. Chemists can leverage the reactivity of 4-Chloro-3-methylquinoline to introduce specific functionalities and structural motifs, opening up possibilities for innovative chemical designs.Overall, 4-Chloro-3-methylquinoline is a versatile and valuable compound in chemical synthesis, with applications spanning the pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and specialty chemical industries. Its role as a key intermediate allows chemists to access a diverse array of functionalized products, making it an essential building block in modern organic synthesis strategies.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com