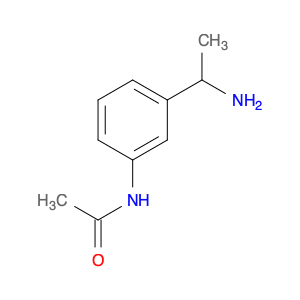
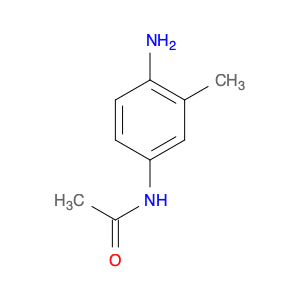
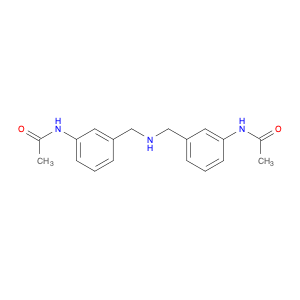
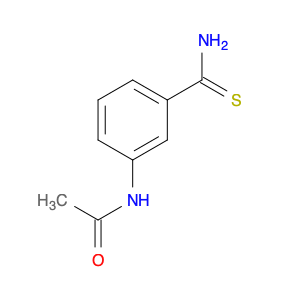
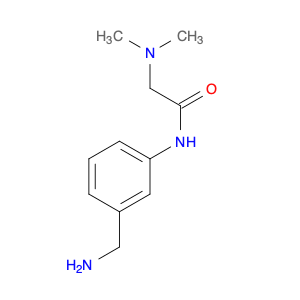
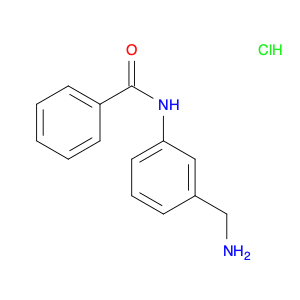
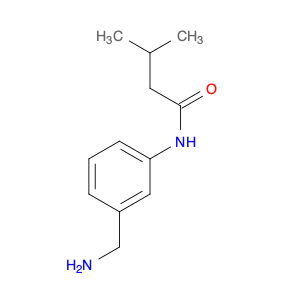
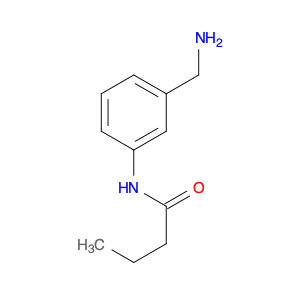
3-Acetylaminobenzylamine, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. Its primary application lies in its role as a key intermediate in the production of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals.This compound plays a crucial role in organic synthesis due to its ability to undergo a range of chemical reactions, including acylation, alkylation, and cyclization. Its versatile nature allows it to serve as a building block for the synthesis of more complex molecules with diverse functionalities.In pharmaceutical chemistry, 3-Acetylaminobenzylamine is often utilized in the preparation of drug candidates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its structural features make it a valuable precursor for the modification of drug molecules to enhance their biological activity, stability, or solubility.Furthermore, in the agrochemical industry, this compound is instrumental in the development of pesticides, herbicides, and other agricultural chemicals. Its reactivity and structural properties make it a valuable tool for creating novel compounds with potent biological activities against pests and diseases affecting crops.Additionally, 3-Acetylaminobenzylamine finds applications in the synthesis of specialty chemicals, such as dyes, pigments, and fragrances. Its ability to participate in various chemical transformations makes it a valuable asset in creating unique and sought-after molecules for a range of industries.Overall, 3-Acetylaminobenzylamine is a versatile and indispensable compound in the realm of chemical synthesis, playing a crucial role in the development of a wide array of products with significant societal impacts.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com