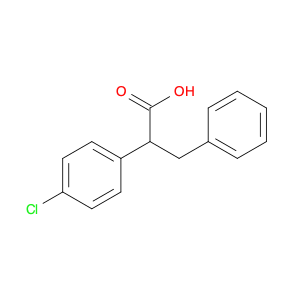
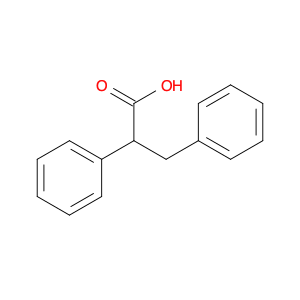
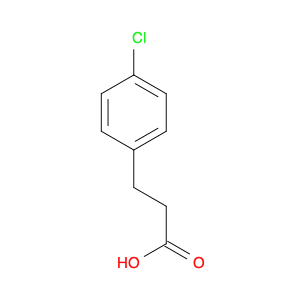
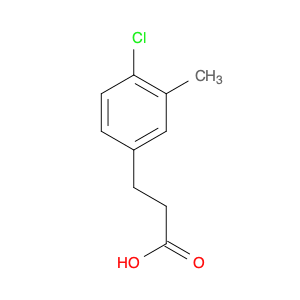
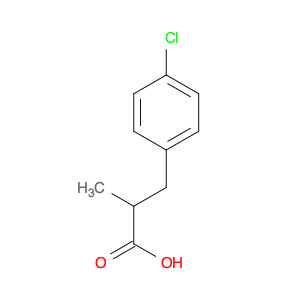
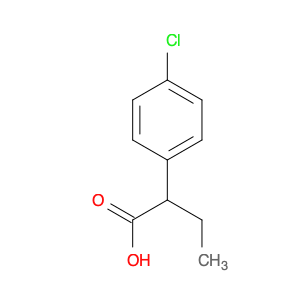
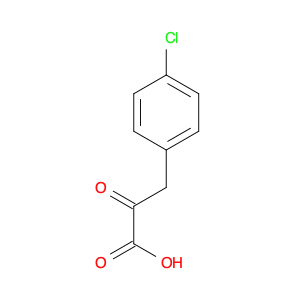
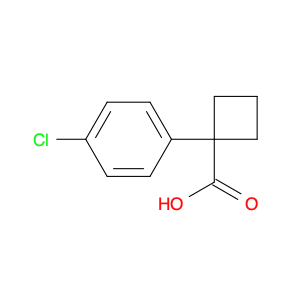
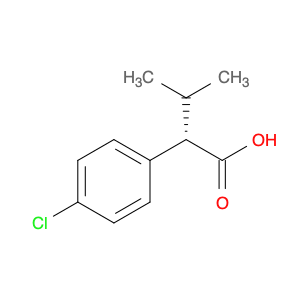
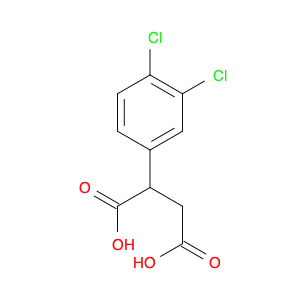
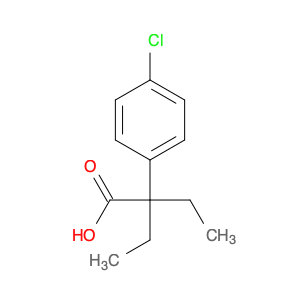
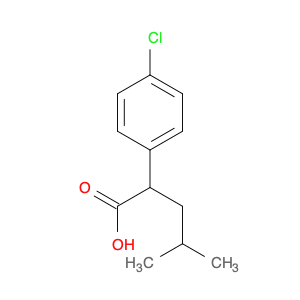
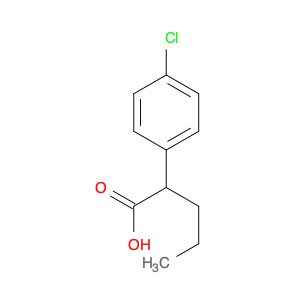
2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenylpropanoic acid, a chemical compound commonly utilized in chemical synthesis, serves a crucial role as a versatile building block in organic chemistry. Leveraging its unique molecular structure, this compound is adept at participating in various synthetic transformations, offering a wide array of applications in the field of organic synthesis.One significant application of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenylpropanoic acid lies in its utilization as a key intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds. Through strategic manipulation of its chemical reactivity, this compound can be transformed into structurally diverse derivatives that are essential for the development of novel drugs. Its ability to undergo functional group modifications makes it a valuable tool for medicinal chemists seeking to design and produce potent therapeutic agents.Furthermore, 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenylpropanoic acid plays a crucial role in the synthesis of advanced materials in materials science. By incorporating this compound into polymerization reactions or cross-coupling processes, researchers can engineer innovative materials with tailored properties, such as enhanced mechanical strength, thermal stability, or conductivity. Its compatibility with a variety of synthetic methodologies makes it an indispensable component in the quest for next-generation materials with precise and controllable characteristics.In summary, the strategic incorporation of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenylpropanoic acid into chemical synthesis processes enables researchers to access a rich palette of functional groups and structural motifs, empowering them to craft intricate molecules, pharmaceuticals, and materials with tailored properties and performance attributes.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com