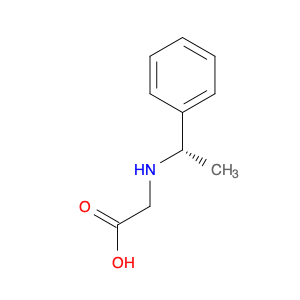
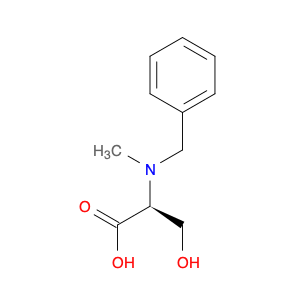
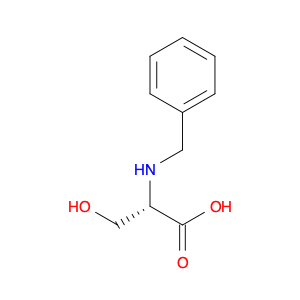
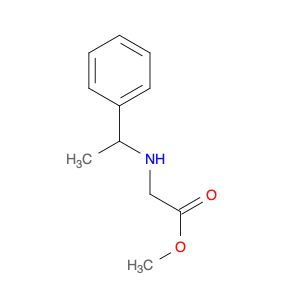
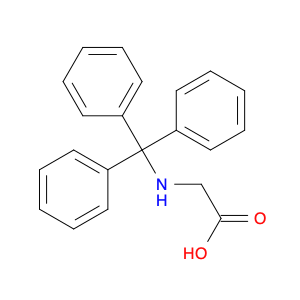
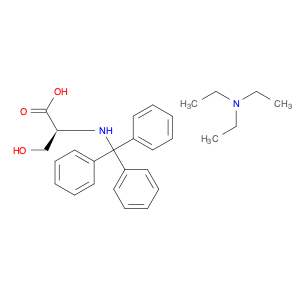
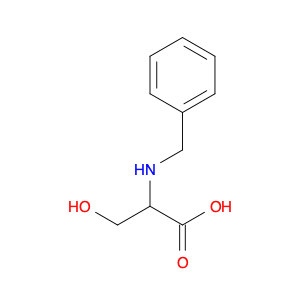
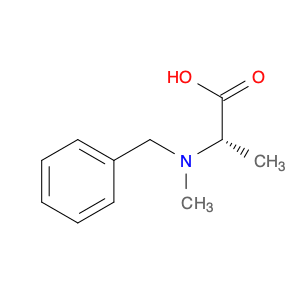
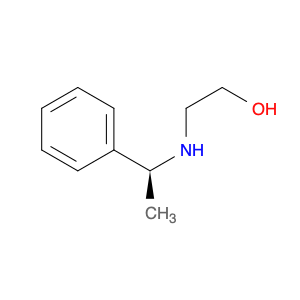
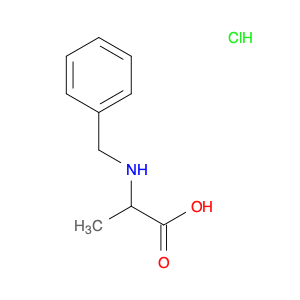
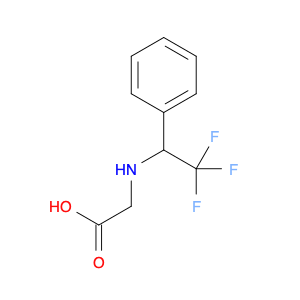
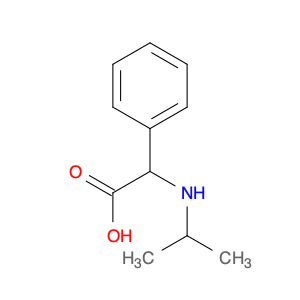
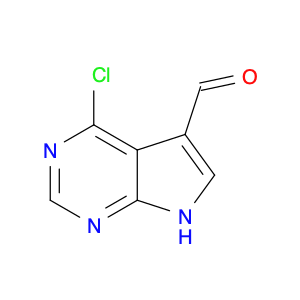
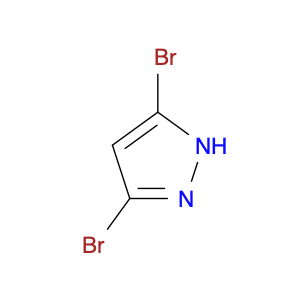
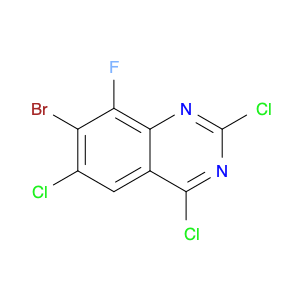
(S)-2-((1-Phenylethyl)amino)acetic acid, also known as enantiomerically pure phenylethylamine, plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis as a chiral building block. Its unique structure allows it to participate in asymmetric reactions, enabling the creation of highly enantioselective compounds.In chemical synthesis, (S)-2-((1-Phenylethyl)amino)acetic acid can be used as a key intermediate in the preparation of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals. Its chiral nature imparts stereochemistry to the final products, making it a valuable tool for the production of optically active compounds. Additionally, this compound can serve as a ligand in asymmetric catalysis, facilitating the formation of chiral molecules with high selectivity.The application of (S)-2-((1-Phenylethyl)amino)acetic acid in chemical synthesis extends to the development of new materials, such as chiral polymers and liquid crystals. By incorporating this chiral building block into the molecular structure, researchers can tailor the properties of the materials and explore novel applications in various fields.Overall, (S)-2-((1-Phenylethyl)amino)acetic acid serves as a versatile tool in chemical synthesis, enabling the efficient and selective construction of complex molecules with defined stereochemistry. Its importance extends across multiple industries, driving innovation and advancement in the realm of organic chemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com