Login |
Create New Account
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com
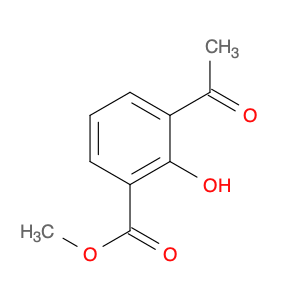
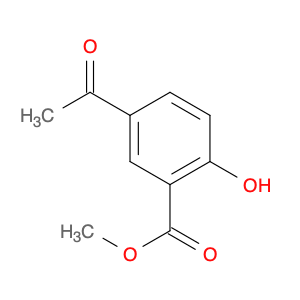
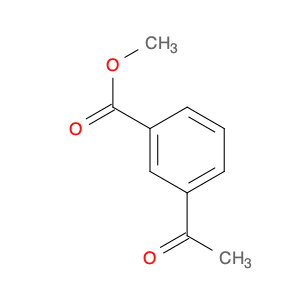
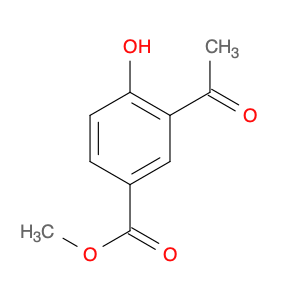
Methyl 3-Acetyl-2-hydroxybenzoate
Catalog#: AR003SFS | CAS#: 77527-00-5 | MDL#: MFCD16883072 | MF: C10H10O4 | MW: 194.184
| Packsize | Purity | Price | Availability | Quantity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg | $105.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 250mg | $123.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 1g | $361.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 5g | $859.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart |
- Description
- Application
- Related Products
- Featured Products
- Safety Information
| Catalog Number | AR003SFS |
| Chemical Name | Methyl 3-Acetyl-2-hydroxybenzoate |
| CAS Number | 77527-00-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H10O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 194.184 |
| MDL Number | MFCD16883072 |
| SMILES | COC(=O)c1cccc(c1O)C(=O)C |
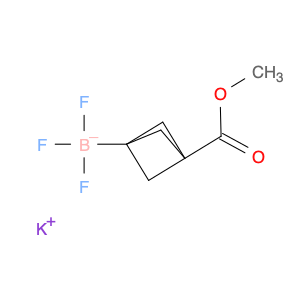
potassium;trifluoro-(3-methoxycarbonyl-1-bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanyl)boranuide
2410559-74-7
| GHS Pictogram |

|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| UN# | N/A |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 |
| Class | N/A |
| Packing Group | N/A |