Login |
Create New Account
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com
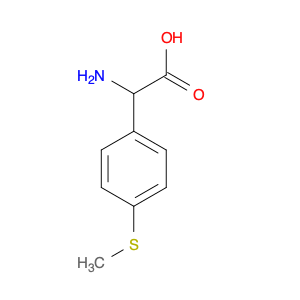
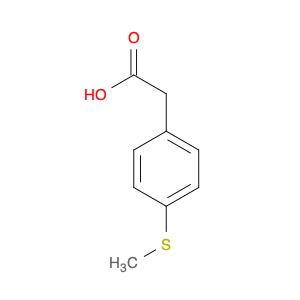
AMINO[4-(METHYLSULFANYL)PHENYL]ACETIC ACID
Catalog#: AR005OKD | CAS#: 7292-80-0 | MDL#: MFCD02662405 | MF: C9H11NO2S | MW: 197.2541
| Availability | ||
|---|---|---|
| Typically In Stock |
- Description
- Application
- Related Products
- Featured Products
| Catalog Number | AR005OKD |
| Chemical Name | AMINO[4-(METHYLSULFANYL)PHENYL]ACETIC ACID |
| CAS Number | 7292-80-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO2S |
| Molecular Weight | 197.2541 |
| MDL Number | MFCD02662405 |
| SMILES | CSc1ccc(cc1)C(C(=O)O)N |