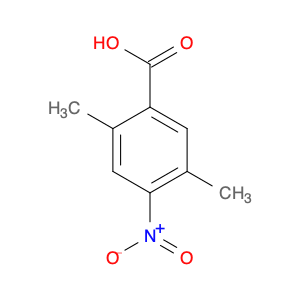
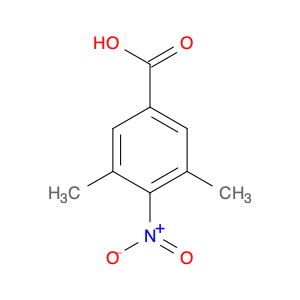
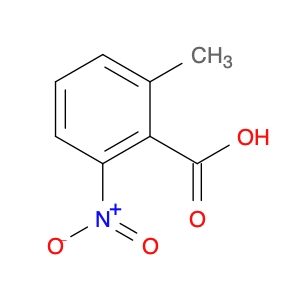
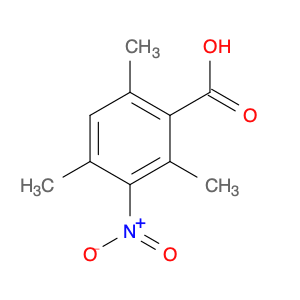
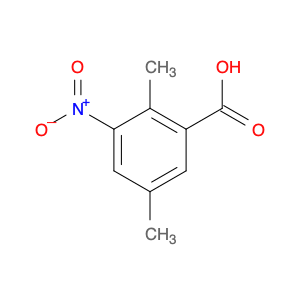
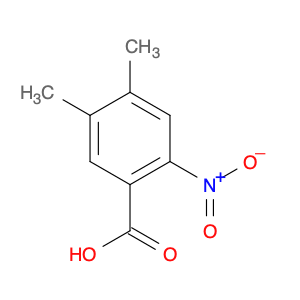
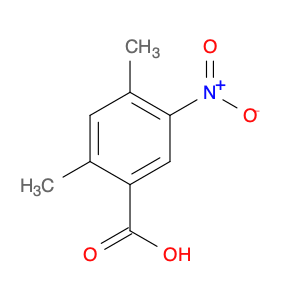
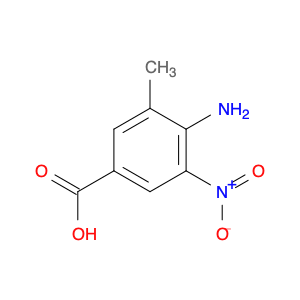
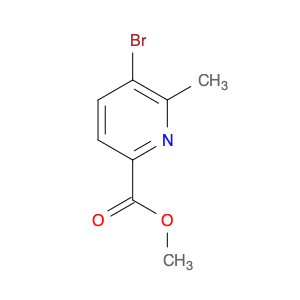
2,5-dimethyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid, also known as DMB acid, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This compound serves as a valuable building block in the preparation of various organic compounds due to its unique properties and reactivity. In chemical synthesis, 2,5-dimethyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid is commonly utilized as a key intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals.One of the primary applications of 2,5-dimethyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid is in the synthesis of substituted benzophenones, which are important structural motifs found in many biologically active compounds. By undergoing selective chemical transformations, DMB acid can be converted into various derivatives of benzophenones, enabling the creation of new pharmaceutical agents and organic molecules with tailored properties. Moreover, the nitro group present in 2,5-dimethyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid can serve as a versatile synthetic handle for further functionalization, allowing chemists to introduce a wide range of chemical functionalities into the final products.Additionally, 2,5-dimethyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid can participate in transition metal-catalyzed reactions, such as Suzuki coupling and Buchwald-Hartwig cross-coupling, to facilitate the construction of complex molecular structures. These reactions enable the incorporation of aryl groups or heteroatoms into the DMB acid framework, expanding the synthetic possibilities and enhancing the diversity of the synthesized compounds. Overall, the strategic use of 2,5-dimethyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid in chemical synthesis offers chemists a valuable tool for accessing structurally diverse and functionally rich molecules with potential applications in drug discovery, materials science, and agrochemical development.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com