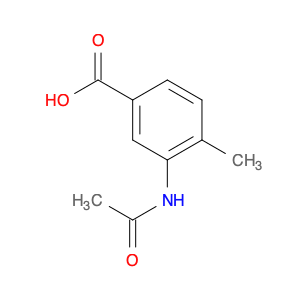
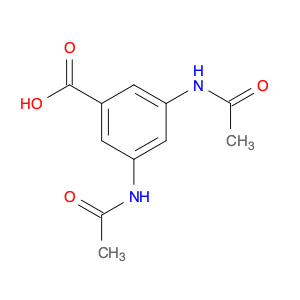
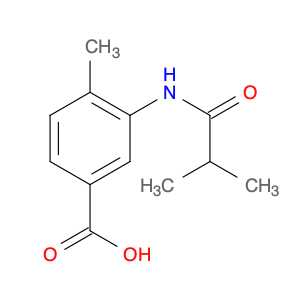
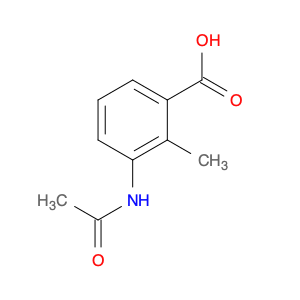
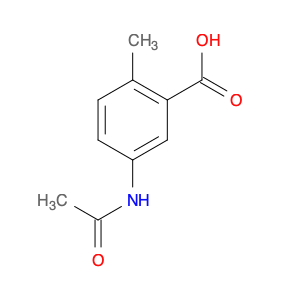
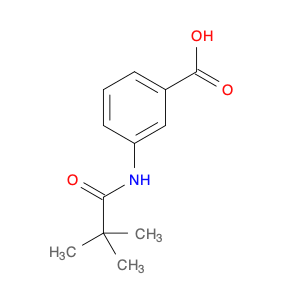
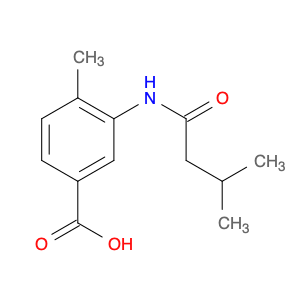
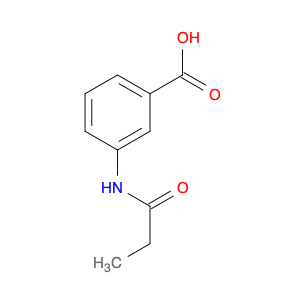
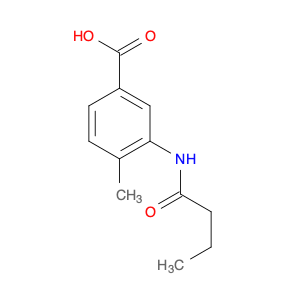
3-Acetamido-4-methylbenzoic acid, also known as AMBA, is a versatile compound commonly used in chemical synthesis for various applications. In organic chemistry, this compound serves as a key building block for the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials. Its unique molecular structure provides the necessary functionality for introducing specific functional groups and modifications into target molecules.One of the primary applications of 3-Acetamido-4-methylbenzoic acid is in the synthesis of custom-designed drug molecules. By incorporating AMBA into the synthesis pathway, chemists can introduce specific functionalities that enhance the biological activity, stability, or solubility of the final drug product. This compound's flexibility allows for the fine-tuning of drug properties, making it a valuable tool in pharmaceutical research and development.Additionally, 3-Acetamido-4-methylbenzoic acid is utilized in the production of specialty chemicals and materials. Its ability to undergo various chemical reactions, such as esterification, amidation, and arylation, makes it a versatile precursor for synthesizing a wide range of organic compounds. Industries that require tailored chemical compounds for specific applications often rely on AMBA as a starting material to achieve the desired product characteristics.Furthermore, in the field of agrochemicals, 3-Acetamido-4-methylbenzoic acid plays a crucial role in the synthesis of pesticide and herbicide molecules. By incorporating this compound into the molecular structure of agricultural chemicals, researchers can create products with enhanced efficacy, targeted delivery, and reduced environmental impact. The precise control over chemical modifications enabled by AMBA facilitates the development of safer and more effective agrochemical formulations.Overall, the strategic utilization of 3-Acetamido-4-methylbenzoic acid in chemical synthesis enables researchers to create sophisticated molecules with tailored properties for various industrial applications. Its versatility, reactivity, and compatibility with diverse synthetic pathways make it a valuable asset in the toolbox of synthetic chemists working towards innovation and discovery.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com