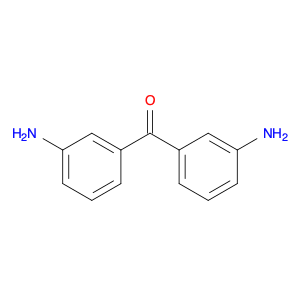
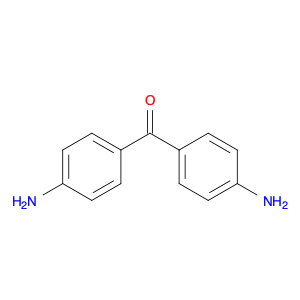
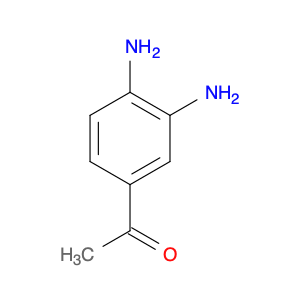
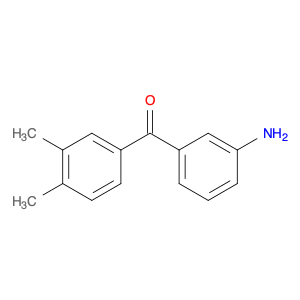
Bis(3-aminophenyl)methanone, also known as BAPM, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis processes. Its unique structure consisting of two 3-aminophenyl groups attached to a central methanone moiety imparts specific properties that make it valuable for various applications.In chemical synthesis, Bis(3-aminophenyl)methanone serves as a key building block for the preparation of complex organic molecules. Its bifunctional nature allows it to participate in diverse reactions, enabling the construction of intricate molecular frameworks with precise control over regioselectivity and stereochemistry.One of the primary applications of Bis(3-aminophenyl)methanone is in the formation of polymeric materials. By utilizing its reactive amino groups, BAPM can be polymerized to generate novel polymeric structures with tailored properties such as mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. These polymers find uses in various industries, including coatings, adhesives, and materials science.Additionally, Bis(3-aminophenyl)methanone plays a crucial role in medicinal chemistry as a potential pharmacophore. Its ability to form diverse intermolecular interactions makes it a valuable scaffold for the design and synthesis of therapeutic agents targeting specific biological receptors or enzymes. By incorporating BAPM-derived motifs into drug molecules, researchers can explore new avenues for drug discovery and development.Overall, the versatility and reactivity of Bis(3-aminophenyl)methanone make it a valuable tool in chemical synthesis, enabling the creation of innovative materials and bioactive compounds with broad applications across various scientific disciplines.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com