Login |
Create New Account
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com
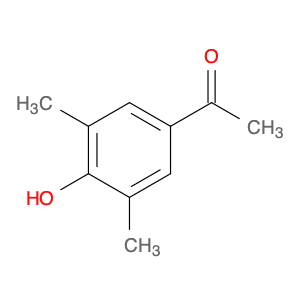
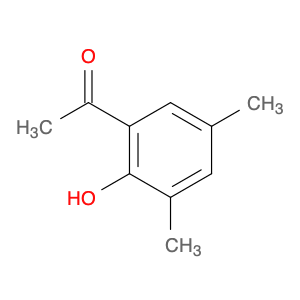
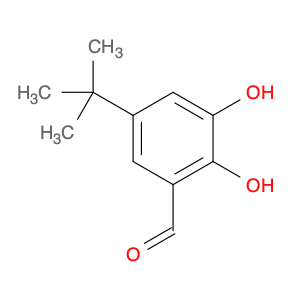
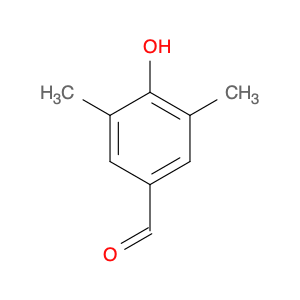
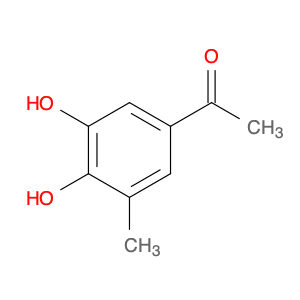
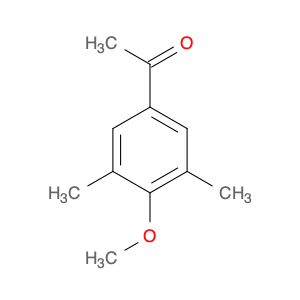
4′-Hydroxy-3′,5′-dimethylacetophenone
Catalog#: AR003LAR | CAS#: 5325-04-2 | MDL#: MFCD00195574 | MF: C10H12O2 | MW: 164.20108
| Packsize | Purity | Price | Availability | Quantity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1g | $24.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 5g | $73.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 10g | $140.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 25g | $222.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 100g | $885.00 | Global Stock | Buy Now | Add To Cart |
- Description
- Application
- Related Products
- Featured Products
| Catalog Number | AR003LAR |
| Chemical Name | 4′-Hydroxy-3′,5′-dimethylacetophenone |
| CAS Number | 5325-04-2 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 164.20108 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00195574 |
| SMILES | CC(=O)c1cc(C)c(c(c1)C)O |
| NSC Number | 109 |
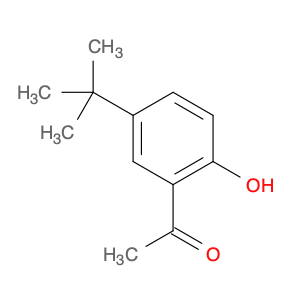
1-[5-(tert-Butyl)-2-hydroxyphenyl]ethan-1-one, 2-Acetyl-4-(tert-butyl)phenol
57373-81-6
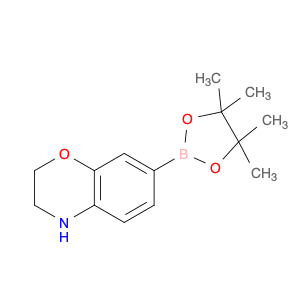
2H-1,4-Benzoxazine, 3,4-dihydro-7-(4,4,5,5-tetraMethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-
1361110-64-6