Login |
Create New Account
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com
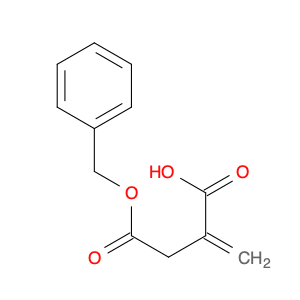
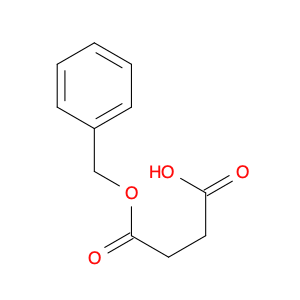
4-(Benzyloxy);-2-methylene-4-oxobutanoic acid
Catalog#: AR006XO2 | CAS#: 48162-88-5 | MDL#: MFCD11553080 | MF: C12H12O4 | MW: 220.2213
| Availability | ||
|---|---|---|
| Typically In Stock |
- Description
- Application
- Related Products
- Featured Products
- Safety Information
| Catalog Number | AR006XO2 |
| Chemical Name | 4-(Benzyloxy);-2-methylene-4-oxobutanoic acid |
| CAS Number | 48162-88-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H12O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 220.2213 |
| MDL Number | MFCD11553080 |
| SMILES | O=C(CC(=C)C(=O)O)OCc1ccccc1 |
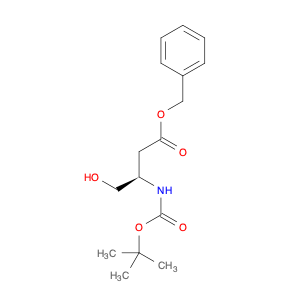
Butanoic acid, 3-[[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]-4-hydroxy-, phenylmethyl ester, (3R)-
182748-72-7
| GHS Pictogram | N/A |
| UN# | - |
| Hazard Statements | - |
| Class | - |
| Packing Group | - |