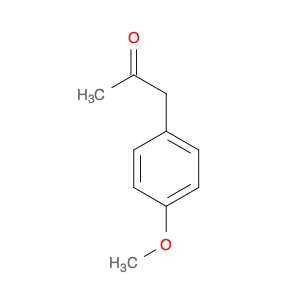
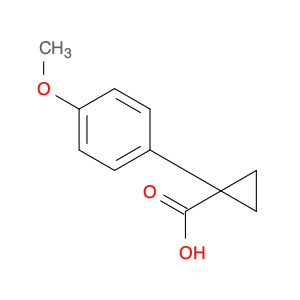
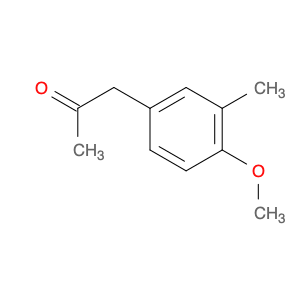
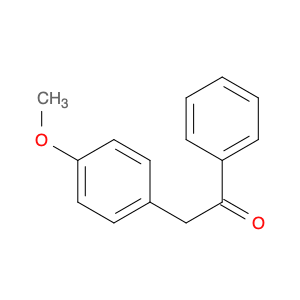
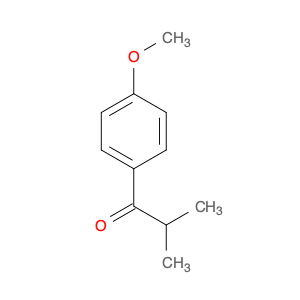
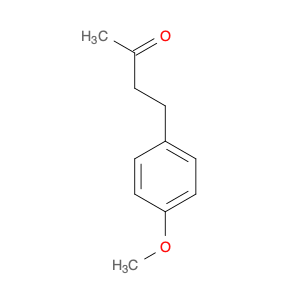
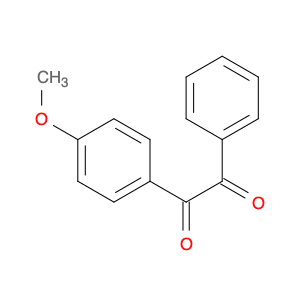
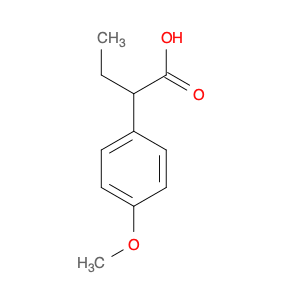
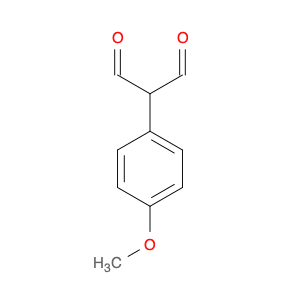
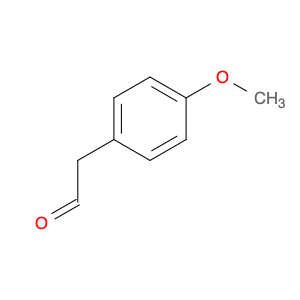
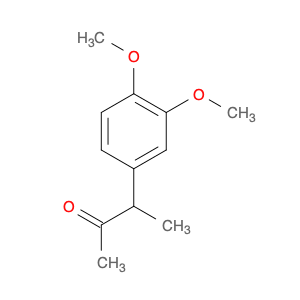
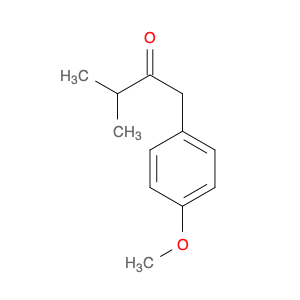
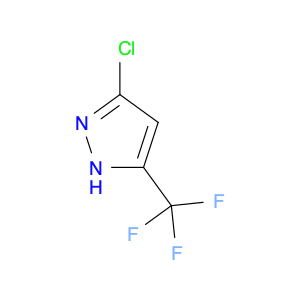
4-Methoxyphenylacetone, also known as p-anisylacetone, is a key intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals. This compound serves as a versatile building block in organic chemistry due to its unique chemical properties and reactivity. In chemical synthesis, 4-Methoxyphenylacetone is commonly utilized as a precursor in the preparation of complex molecules through different synthetic routes.One of the main applications of 4-Methoxyphenylacetone is in the synthesis of Amphetamines, where it serves as a crucial intermediate in the production of substances such as methamphetamine. By undergoing various chemical transformations, 4-Methoxyphenylacetone can be converted into different derivatives, thereby enabling the synthesis of diverse amphetamine-based compounds. Additionally, this compound can be used in the synthesis of other pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and agrochemicals, showcasing its versatility in organic synthesis.Furthermore, 4-Methoxyphenylacetone can participate in various synthetic reactions, such as Grignard additions, nucleophilic substitutions, and oxidative transformations, making it a valuable compound for chemists in the design and development of novel molecules. Its structural features, including the methoxy and phenyl groups, provide a platform for the introduction of different functional groups, leading to the creation of structurally diverse organic compounds with desired properties.Overall, the application of 4-Methoxyphenylacetone in chemical synthesis highlights its significance as a key intermediate for the preparation of various biologically active compounds and fine chemicals. Its role in constructing complex molecules underscores its importance in the field of organic chemistry, offering opportunities for innovation and discovery in drug development and material science.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com