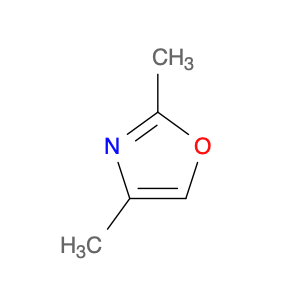
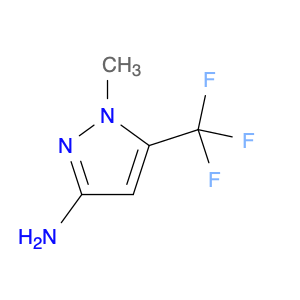
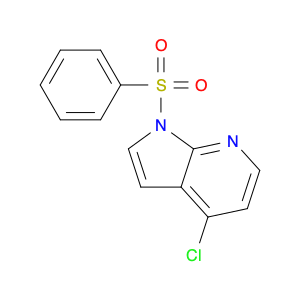
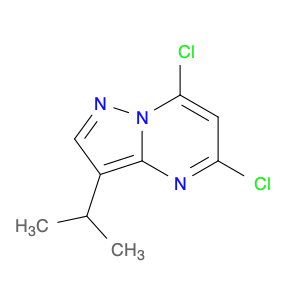
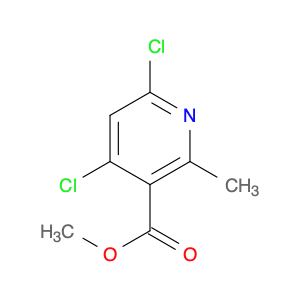
2,4-Dimethyloxazole, also known as dimethyl-2-oxazoline, is a versatile compound that finds frequent application in chemical synthesis, particularly in the formation of heterocyclic compounds. This organic compound consists of a five-membered ring containing one oxygen and one nitrogen atom.In chemical synthesis, 2,4-Dimethyloxazole is commonly employed as a building block or intermediate in the preparation of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other specialty chemicals. Its unique structure and reactivity make it a valuable reagent for the synthesis of various drug candidates and bioactive molecules. The incorporation of 2,4-Dimethyloxazole units into organic molecules can impart desired properties and functionalities, leading to the development of new materials and compounds with potential industrial applications.Additionally, 2,4-Dimethyloxazole can serve as a precursor for the synthesis of more complex heterocyclic compounds through various transformation reactions. Its ability to undergo functional group interconversions and participate in multi-step synthetic pathways makes it a versatile tool in the hands of organic chemists. By utilizing 2,4-Dimethyloxazole in chemical synthesis, researchers can access a diverse array of molecular structures with tailored properties and activities, contributing to advancements in the fields of pharmaceuticals, materials science, and agrochemicals.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com