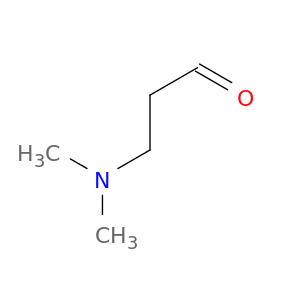
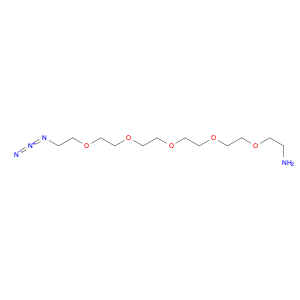
3-(Dimethylamino)propanal, also known as DMAP, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. Its primary application lies in its role as a key building block in the creation of various complex organic molecules. DMAP is particularly valued for its ability to serve as a precursor in the formation of a variety of heterocyclic compounds, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Additionally, in the field of medicinal chemistry, 3-(Dimethylamino)propanal is employed as a crucial intermediate in the synthesis of biologically active compounds, such as anti-cancer agents, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Its unique chemical properties enable it to participate in a diverse range of reactions, including acylation, alkylation, and condensation reactions, making it an essential component in the toolbox of synthetic chemists. Furthermore, 3-(Dimethylamino)propanal plays a significant role in the development of novel materials, such as polymers, pigments, and dyes, due to its reactive nature and compatibility with various synthetic methodologies. Its widespread applicability in chemical synthesis underscores its importance as a valuable reagent for producing diverse compounds with specific desired properties.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com