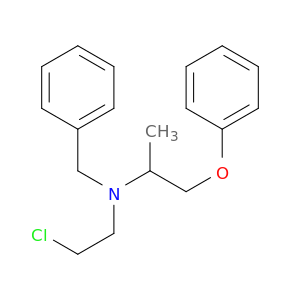
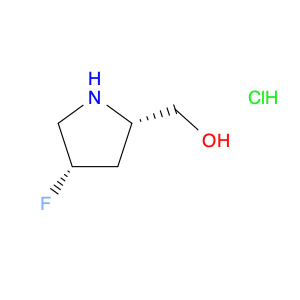
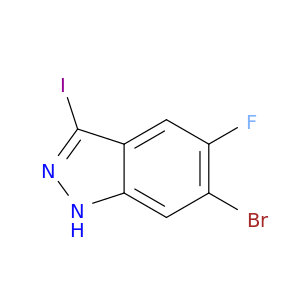
(±)-Phenoxybenzamine, a key compound in chemical synthesis, is a versatile building block utilized in the production of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its unique chemical properties make it an essential component in the creation of complex organic molecules.One primary application of (±)-Phenoxybenzamine in chemical synthesis is as a key intermediate in the preparation of synthetic organic compounds. This compound serves as a crucial starting material for the synthesis of diverse structures by undergoing various chemical transformations such as functional group interconversions, stereochemistry modifications, and complex scaffold constructions.Furthermore, (±)-Phenoxybenzamine plays a pivotal role in the development of novel drug candidates. By incorporating this compound into the molecular structure of pharmaceuticals, chemists can optimize the pharmacological properties, enhance the bioavailability, and improve the therapeutic efficacy of the resulting drugs. Its presence often leads to the creation of potent and selective compounds with targeted biological activities.In agrochemical synthesis, (±)-Phenoxybenzamine is employed to design innovative pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides. By utilizing its chemical reactivity and versatility, researchers can create environmentally friendly and effective agricultural chemicals that help protect crops from pests and diseases while minimizing adverse impacts on the ecosystem.Overall, the application of (±)-Phenoxybenzamine in chemical synthesis is indispensable for the generation of a wide range of important compounds with significant implications in the fields of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its versatility, reactivity, and structural features make it a valuable tool for chemists seeking to develop new and improved products with unique functionalities and applications.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com