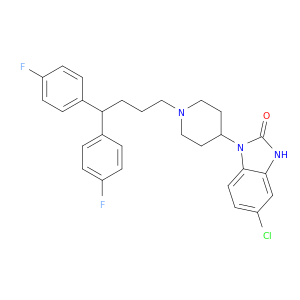
The chemical compound 1-[1-[4,4-Bis(4-fluorophenyl)butyl]-4-piperidinyl]-5-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis processes due to its unique structural characteristics and functional groups. It serves as a versatile building block for the creation of various complex molecules in organic chemistry. Specifically, this compound can be utilized as a key intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceutical substances, agrochemicals, and advanced materials.The presence of the piperidine moiety in the structure of this compound offers reactivity and selectivity in forming cyclic structures or functionalized amines through various chemical reactions such as reductive amination, nucleophilic substitution, and ring-closing reactions. Additionally, the benzimidazole ring system provides opportunities for further diversification through transformations like halogenation, alkylation, and Suzuki coupling reactions.Moreover, the fluorophenyl substituents on the butyl chain can serve as directing groups in metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, enabling the introduction of additional functional groups or stereochemical control in the synthesis of complex molecules. The chloro substituent on the benzimidazole ring can participate in nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions, facilitating the introduction of diverse functionalities and structural modifications.Overall, the strategic placement of different functional groups within the molecular framework of 1-[1-[4,4-Bis(4-fluorophenyl)butyl]-4-piperidinyl]-5-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one offers chemists a versatile platform for designing and synthesizing novel compounds with tailored properties and applications in various fields of chemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com