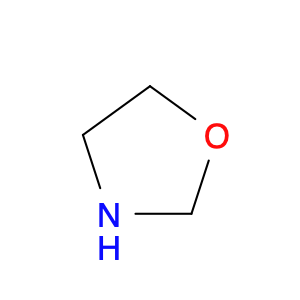
Oxazolidine is a versatile and highly valuable compound in chemical synthesis due to its reactivity and unique chemical properties. This cyclic organic compound is commonly utilized as a key building block in the creation of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals.One of the primary applications of oxazolidine in chemical synthesis is as a protecting group for amines. By forming a stable oxazolidine derivative with an amine functional group, it effectively masks the amine functionality, allowing for selective chemical reactions to occur without interference from the amine group. This protection-deprotection strategy is crucial in the synthesis of complex organic molecules, as it enables chemists to control the reactivity of specific functional groups.Furthermore, oxazolidine is utilized as a chiral auxiliary in asymmetric synthesis processes. Its ability to induce chirality and control the stereochemistry of reactions makes it a valuable tool in the preparation of enantiomerically pure compounds. By incorporating oxazolidine into the reaction scheme, chemists can achieve high levels of stereocontrol, leading to the formation of optically active products with high enantiomeric excess.In addition to its role in protecting groups and asymmetric synthesis, oxazolidine can also serve as a versatile intermediate for the construction of heterocyclic compounds. Its unique ring structure and reactivity make it a valuable precursor in the synthesis of diverse molecular scaffolds, providing access to a wide range of functionalized molecules with potential applications in drug discovery and material science.Overall, the application of oxazolidine in chemical synthesis spans across various domains of organic chemistry, highlighting its significance as a key reagent for the strategic construction of complex molecular architectures.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com