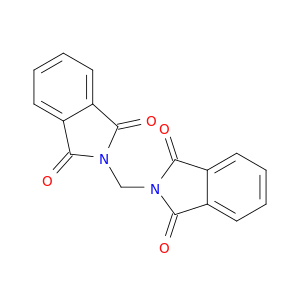
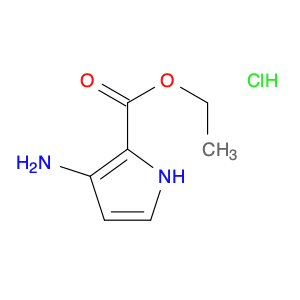
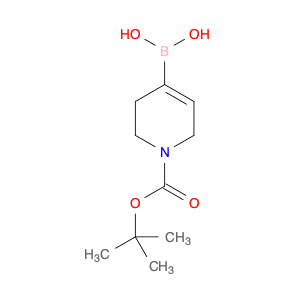
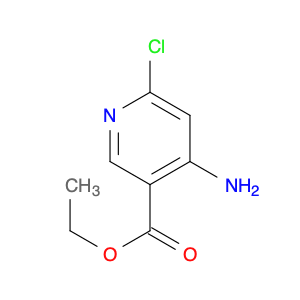
The compound 2,2'-methylenebis(1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione), also known as $name$, serves as a versatile building block in chemical synthesis due to its unique structure and reactivity. This compound is commonly used as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various organic molecules, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals and advanced materials.In chemical synthesis, $name$ can act as a bifunctional molecule capable of participating in multiple reactions simultaneously, allowing for the efficient construction of complex molecular structures. Its ability to undergo nucleophilic addition reactions and form covalent bonds with other molecules makes it a valuable tool for organic chemists seeking to design and create novel compounds with specific properties.Furthermore, the presence of multiple reactive sites in $name$ enables the incorporation of diverse functional groups and substituents, offering a high degree of synthetic flexibility and control over the final product's properties. Whether used as a coupling reagent, a masked carbonyl compound, or a reactive intermediate, $name$ plays a crucial role in enabling the synthesis of diverse chemical entities with tailored functionalities and applications.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com