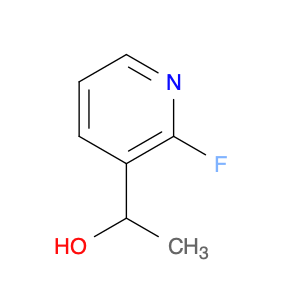
1-(2-Fluoropyridin-3-yl)ethanol, also known as $name$, is a key intermediate used in organic chemical synthesis. This compound plays a crucial role in the development of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals. Its unique structure containing a fluoropyridine ring and an alcohol functional group makes it a versatile building block for synthesizing more complex molecules.In chemical synthesis, $name$ serves as a valuable starting material for the preparation of heterocyclic compounds, which are essential components in drug discovery and agricultural chemistry. Its fluoropyridine moiety can participate in diverse transformations, offering opportunities for further structural modifications to enhance the desired properties of the final product. Additionally, the presence of the alcohol group provides a handle for introducing additional chemical functionalities, such as esters, ethers, or amines, through various synthetic reactions.Beyond its significance as a synthetic intermediate, the incorporation of 1-(2-Fluoropyridin-3-yl)ethanol into target molecules can impart specific biological activities or physical properties, making it an indispensable tool for medicinal chemistry and material science research. Overall, the utilization of $name$ in chemical synthesis demonstrates its importance in creating innovative compounds with potential applications in various industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com