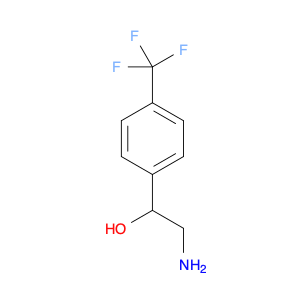
2-Amino-1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ethanol, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound that finds wide applications in chemical synthesis. This compound is frequently used as a key building block in the preparation of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials.Due to its unique structure and functional groups, $name$ serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of diverse organic compounds. One of its key applications is in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds, which are important in drug discovery and development. By serving as a starting material in the construction of complex molecules, $name$ plays a crucial role in the creation of new drugs and therapeutics.Additionally, the presence of the trifluoromethyl group in the molecule enhances its lipophilicity and bioavailability, making it an attractive candidate for modification and optimization in medicinal chemistry. Chemists can leverage the versatility of $name$ to introduce specific functionalities and tailor its properties according to the desired application.Furthermore, the amino and hydroxyl groups present in the molecule can participate in a variety of chemical reactions, enabling the synthesis of diverse derivatives with tailored properties. These derivatives can exhibit a range of biological activities, making them valuable tools in biological research and drug design.In summary, the strategic placement of functional groups in 2-Amino-1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ethanol confers it with significant utility in chemical synthesis, particularly in the creation of medicinal compounds and materials with tailored properties. Its versatility and synthetic accessibility make it a valuable asset in the toolkit of organic chemists striving to develop novel molecules with potential applications in various fields.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com