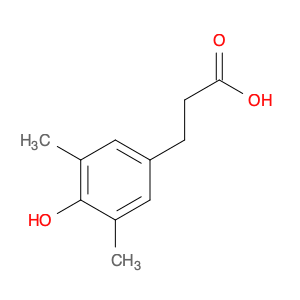
The 3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)propanoic Acid, also known as $name$, is a crucial compound commonly utilized in chemical synthesis processes. This compound plays a significant role in the field of organic chemistry due to its versatile applications.Firstly, $name$ is frequently employed as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds. Its structural properties make it an essential building block for the production of pharmaceuticals with diverse therapeutic applications. By incorporating $name$ into the synthesis routes, chemists can access a wide range of potential drug candidates with enhanced bioavailability and efficacy.Additionally, $name$ is a valuable reagent in the preparation of specialty chemicals and fine organic products. Its unique chemical reactivity allows for selective functionalization reactions, enabling chemists to introduce specific functional groups at precise positions within a molecule. This control over chemical transformations is essential in the design and synthesis of specialty chemicals used in industries such as agrochemicals, flavors, and fragrances.Moreover, $name$ serves as a crucial tool in the development of novel materials with tailored properties. By utilizing $name$ as a starting material in polymer synthesis, chemists can engineer materials with specific mechanical, thermal, and optical characteristics. This versatility makes $name$ an essential component in the production of advanced materials for various applications ranging from coatings and adhesives to electronics and biomedical devices.In conclusion, the 3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)propanoic Acid, or $name$, is a pivotal compound in chemical synthesis with widespread applications in pharmaceutical, specialty chemical, and material science industries. Its role as a versatile building block and reagent highlights its importance in advancing scientific research and innovation within the field of organic chemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com