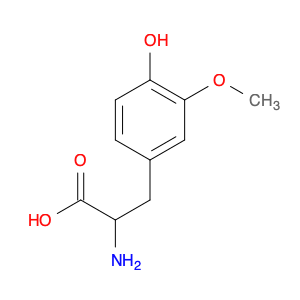
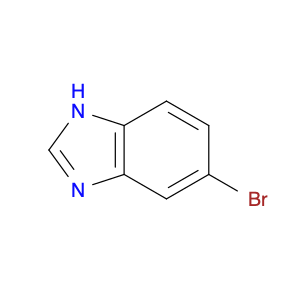
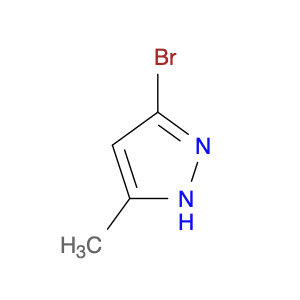
2-Amino-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propanoic acid, also known as AHMPA, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. It serves as a key building block in the production of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. AHMPA's unique chemical structure allows it to participate in a wide range of reactions, making it a valuable tool for chemists in the synthesis of complex organic molecules.One of the primary applications of AHMPA in chemical synthesis is its role as a precursor in the synthesis of biologically active compounds. By incorporating AHMPA into the chemical structure of a molecule, chemists can introduce specific functional groups and stereochemical elements that are crucial for the desired biological activity. This enables the creation of novel drug candidates, pesticides, and other bioactive molecules with enhanced potency and selectivity.Furthermore, AHMPA can be utilized as a chiral auxiliary in asymmetric synthesis. Its stereochemistry can influence the stereochemical outcome of a reaction, allowing for the selective formation of desired enantiomers. This ability is particularly valuable in the production of pharmaceuticals, where the stereochemistry of a molecule can significantly impact its pharmacological properties.In summary, 2-Amino-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propanoic acid plays a vital role in chemical synthesis by serving as a versatile building block for the construction of complex organic molecules with specific biological activities and stereochemical properties. Its applications extend across various industries, making it an indispensable tool for chemists engaged in the development of new and innovative substances.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com