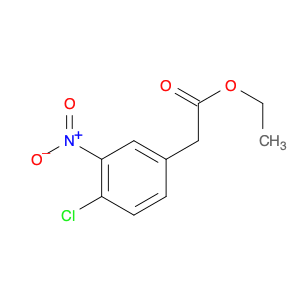
Ethyl 2-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)acetate is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis. This compound serves as a crucial building block in the creation of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and various fine chemicals. Its unique structure, containing both an aromatic chlorine group and a nitro group, imparts specific reactivity that enables it to participate in a multitude of synthetic pathways.In the realm of organic chemistry, ethyl 2-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)acetate can undergo various transformations such as nucleophilic substitution, reduction, and coupling reactions. These reactions allow for the introduction of diverse functional groups, facilitating the production of complex molecules with desired properties. Furthermore, the presence of the nitro group provides a handle for further modifications through reduction to the corresponding amine or conversion to other functional groups.One notable application of ethyl 2-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)acetate is its utility in the synthesis of bioactive compounds and pharmaceutical intermediates. By incorporating this compound into synthetic routes, chemists can access key structural motifs found in many biologically active molecules. This enables the efficient production of potential drug candidates or valuable intermediates for further elaboration.Moreover, in agrochemical synthesis, ethyl 2-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)acetate plays a crucial role in the development of crop protection agents and pesticides. Its versatile nature allows for the construction of specialized molecules with pesticidal properties, contributing to the enhancement of agricultural productivity and sustainability.Overall, the application of ethyl 2-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)acetate in chemical synthesis underscores its significance as a strategic intermediate with diverse reactivity and synthetic potential. Its versatility and utility make it a valuable tool for chemists working in drug discovery, agrochemical development, and the synthesis of fine chemicals.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com