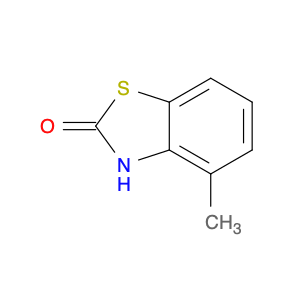
4-Methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2(3H)-one, also known as $name$, serves as a versatile building block in chemical synthesis due to its unique chemical structure and reactivity. This compound is frequently utilized as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds with valuable pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and materials science applications.One prominent application of 4-Methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2(3H)-one is in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. By incorporating this molecule as a starting material, chemists can access a diverse array of heterocyclic structures, which are essential components in many biologically active compounds. The presence of the thiazole ring in 4-Methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2(3H)-one provides an opportunity for the introduction of additional functional groups through chemical transformations, allowing for the creation of new molecules with tailored properties.Furthermore, 4-Methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2(3H)-one can participate in various types of reactions, such as substitution, addition, and cyclization, enabling its use in the construction of complex molecular frameworks. Its versatility in chemical reactions makes it a valuable reagent in the synthesis of diverse organic molecules with significant commercial and scientific implications.In summary, 4-Methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2(3H)-one plays a crucial role in the field of chemical synthesis by serving as a key intermediate for the production of heterocyclic compounds with wide-ranging applications in various industries. Its unique structure and reactivity make it an indispensable building block for the design and preparation of novel organic molecules with targeted properties.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com