Login |
Create New Account
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com
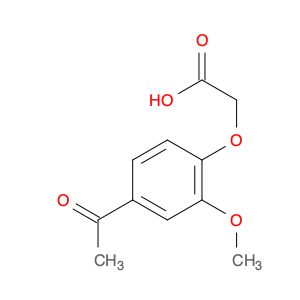
(4-ACETYL-2-METHOXY-PHENOXY)-ACETIC ACID
Catalog#: AR00FGB6 | CAS#: 68461-48-3 | MDL#: MFCD01318192 | MF: C11H12O5 | MW: 224.21
| Packsize | Purity | Price | Availability | Quantity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg | $83.00 | 2-3 weeks | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 100mg | $116.00 | 2-3 weeks | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 250mg | $152.00 | 2-3 weeks | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 500mg | $266.00 | 2-3 weeks | Buy Now | Add To Cart | ||
| 1g | $377.00 | 2-3 weeks | Buy Now | Add To Cart |
- Description
- Application
- Related Products
- Featured Products
| Catalog Number | AR00FGB6 |
| Chemical Name | (4-ACETYL-2-METHOXY-PHENOXY)-ACETIC ACID |
| CAS Number | 68461-48-3 |
| Molecular Formula | C11H12O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 224.21 |
| MDL Number | MFCD01318192 |
| SMILES | COc1cc(ccc1OCC(=O)O)C(=O)C |