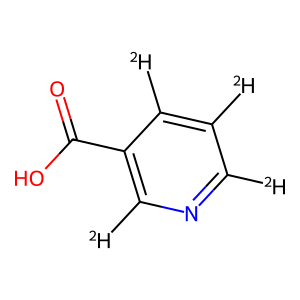
3-Pyridine-2,4,5,6-d4-carboxylic acid is a deuterated derivative of 3-pyridinecarboxylic acid, a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. Its unique isotopic composition makes it a valuable tool in various research applications.In chemical synthesis, 3-Pyridine-2,4,5,6-d4-carboxylic acid serves as a stable isotope-labeled building block that can be incorporated into organic molecules to track reaction pathways and mechanisms. Its deuterium atoms provide distinct spectroscopic signatures, enabling precise tracking of the compound during multi-step synthesis processes.Additionally, the deuterated form of 3-pyridinecarboxylic acid offers enhanced stability and resistance to metabolic degradation in biological studies. This property makes it particularly useful in drug development research, where understanding the fate and behavior of drug molecules in biological systems is crucial.Furthermore, the isotopic labeling of 3-Pyridine-2,4,5,6-d4-carboxylic acid can aid in elucidating molecular structures through techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. By introducing deuterium into specific positions of the molecule, researchers can gather valuable insights into the conformational dynamics and interactions of complex organic compounds.Overall, the application of 3-Pyridine-2,4,5,6-d4-carboxylic acid in chemical synthesis offers a powerful tool for studying complex molecular systems, probing reaction mechanisms, and advancing research in diverse fields of chemistry and biochemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com