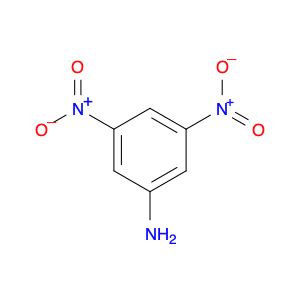
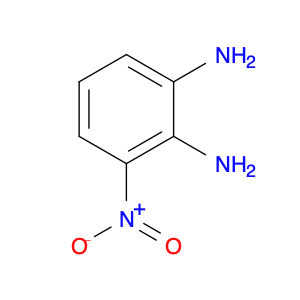
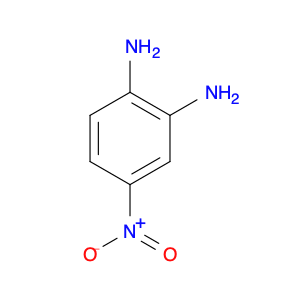
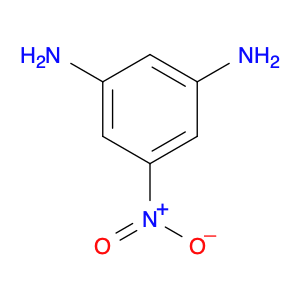
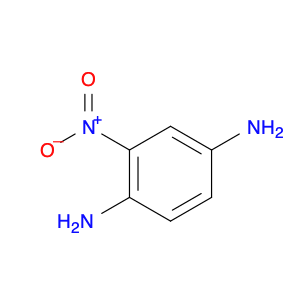
3,5-Dinitroaniline, also known as DNA, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. It serves a crucial role as a building block in the production of various organic chemicals. In particular, 3,5-dinitroaniline is commonly employed in the synthesis of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural chemicals.In chemical synthesis, 3,5-dinitroaniline functions as a key intermediate in the formation of complex organic molecules. Its unique chemical properties make it a valuable precursor in reactions that lead to the creation of important compounds used in different industries. By incorporating 3,5-dinitroaniline into synthetic pathways, chemists can efficiently access a diverse range of products with specific applications.Furthermore, the reactivity of 3,5-dinitroaniline enables chemists to modify its structure through various chemical transformations, allowing for the development of tailored molecules for specific purposes. This flexibility makes 3,5-dinitroaniline a valuable tool in the hands of synthetic chemists seeking to design novel materials with desired properties.In summary, 3,5-Dinitroaniline plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis by serving as a versatile building block for the production of a wide array of organic compounds used in diverse applications across industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com