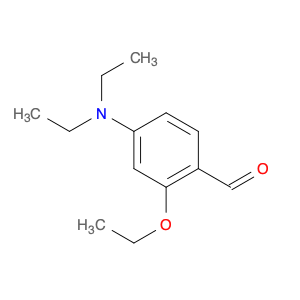
Benzaldehyde, 4-(diethylamino)-2-ethoxy-, is a versatile compound frequently utilized in chemical synthesis for its unique properties and reactivity. This compound serves as a valuable building block in the creation of various organic compounds due to its ability to participate in a wide range of chemical reactions. With its benzaldehyde functionality, the molecule provides a source of aromaticity and acts as an electrophile in reactions such as nucleophilic additions and condensations.In chemical synthesis, Benzaldehyde, 4-(diethylamino)-2-ethoxy-, can undergo reactions with a variety of nucleophiles, such as amines, alcohols, and organometallic reagents, to form new compounds with different functional groups. Its diethylamino and ethoxy substituents contribute to the compound's overall reactivity and allow for the introduction of diverse chemical functionalities during synthesis. This reactivity makes Benzaldehyde, 4-(diethylamino)-2-ethoxy-, an essential component in the construction of complex organic molecules and pharmaceutical intermediates.Furthermore, the electrophilic nature of benzaldehyde in this compound enables its participation in classic organic reactions like Grignard reactions, Wittig reactions, and Cannizzaro reactions. These reactions broaden the scope of applications for Benzaldehyde, 4-(diethylamino)-2-ethoxy-, in chemical transformations, enabling chemists to access a wide array of structurally diverse compounds efficiently.Overall, the strategic incorporation of Benzaldehyde, 4-(diethylamino)-2-ethoxy-, in chemical synthesis allows for the seamless construction of intricate organic molecules with diverse functionalities, making it a valuable reagent in the hands of synthetic chemists.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com