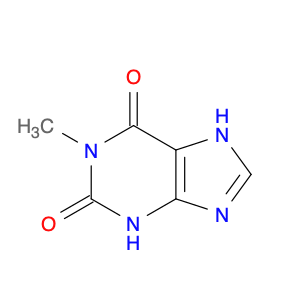
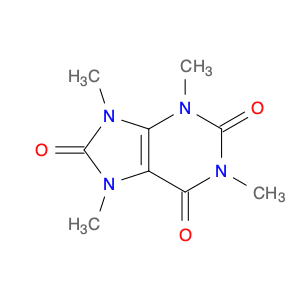
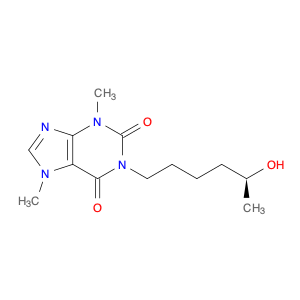
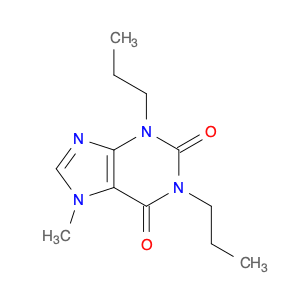
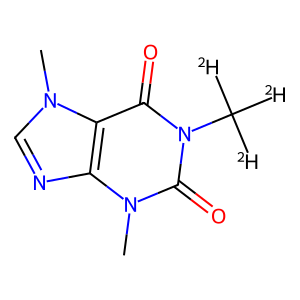
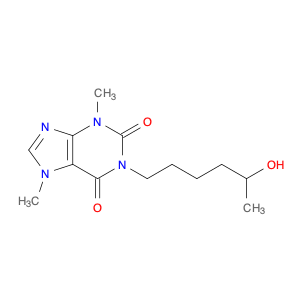
1-Methyl-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione, commonly known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis. Its unique molecular structure and reactivity make it a valuable building block for the creation of various organic compounds.In chemical synthesis, $name$ serves as an important intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its ability to undergo diverse chemical reactions enables the formation of complex molecular structures with specific functionalities. Due to its electron-rich purine ring system, $name$ can participate in nucleophilic addition reactions, providing opportunities for the introduction of new functional groups.$name$ is particularly valuable in the synthesis of purine-based compounds, such as nucleosides and nucleotides, which are essential components of DNA and RNA. By incorporating $name$ into synthetic pathways, chemists can access a wide range of purine derivatives with tailored properties for various applications in the fields of medicine, agriculture, and materials science.Furthermore, the reactivity of $name$ allows for the modification of its chemical structure to generate analogs with enhanced biological activities or improved physicochemical properties. This versatility makes $name$ a valuable tool for medicinal chemists seeking to design novel drug candidates with optimized efficacy and safety profiles.Overall, the application of 1-Methyl-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione in chemical synthesis offers a pathway to the creation of diverse organic compounds with tailored functionalities and applications across different industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com