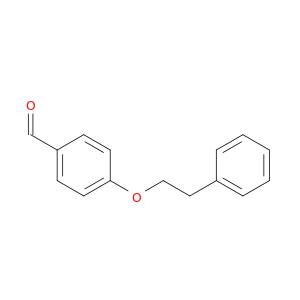
4-(2-Phenylethoxy)benzaldehyde is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis as a key building block for the creation of various organic compounds. This aldehyde derivative possesses a phenyl ring attached to a benzene ring through an oxygen atom, providing unique opportunities for structural modification and functionalization in synthesis pathways.In organic chemistry, 4-(2-phenylethoxy)benzaldehyde serves as a valuable starting material for the preparation of diverse aromatic compounds, such as substituted benzaldehydes, ketones, and heterocycles. Its aldehyde functional group allows for further derivatization through a variety of chemical reactions, including Grignard reactions, aldol condensations, and Wittig reactions, enabling the synthesis of more complex molecules with tailored properties.Moreover, the presence of the phenylethoxy moiety in this compound imparts specific reactivity and steric effects that can be strategically leveraged in organic transformations to achieve desired molecular structures and properties. By carefully selecting reaction conditions and coupling partners, chemists can exploit the unique reactivity profile of 4-(2-phenylethoxy)benzaldehyde to access a diverse array of functionalized products with added value in various applications.Overall, 4-(2-phenylethoxy)benzaldehyde plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis as a versatile building block with significant potential for the development of novel organic compounds across different industries, ranging from pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals to materials science and beyond.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com