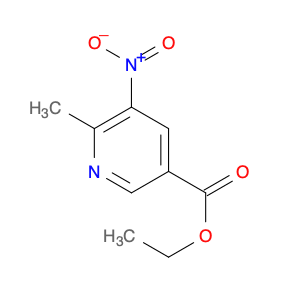
The compound 1-(1H-Benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)ethanone, also known as $name$, plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis as a versatile building block. Its unique structure containing both a benzimidazole ring and a ketone functional group makes it a valuable intermediate for the synthesis of various organic compounds.In chemical synthesis, $name$ is commonly used as a key starting material for the preparation of heterocyclic compounds with diverse biological activities. Its benzimidazole moiety provides opportunities for the formation of complex structures through various reactions, such as nucleophilic substitution, cyclization, and condensation reactions.Additionally, the ketone group in $name$ can undergo a range of transformations, including reduction, oxidation, and functional group manipulations, allowing for further diversification of its chemical properties. This enables chemists to modify the structure of $name$ to tailor its reactivity and selectivity for specific synthetic pathways.Overall, the strategic incorporation of 1-(1H-Benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)ethanone in chemical synthesis provides a powerful platform for the construction of novel molecules with potential applications in medicinal chemistry, material science, and other fields of research.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com