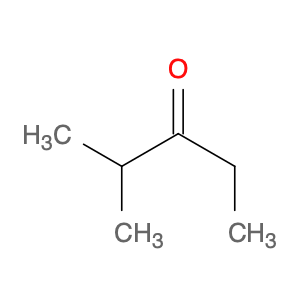
2-Methylpentan-3-one, also known as diisobutyl ketone, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This ketone serves as a valuable building block in organic chemistry due to its unique structure and reactivity. In organic synthesis, 2-methylpentan-3-one can undergo a variety of reactions to form complex molecules with diverse functionalities.One primary application of 2-methylpentan-3-one in chemical synthesis is as a solvent. Its medium boiling point and good solubility properties make it an excellent choice for dissolving a wide range of organic compounds. This feature is particularly useful in reactions where precise control of reaction conditions is crucial for the formation of desired products.Additionally, 2-methylpentan-3-one can act as a carbonyl source in various transformations. Through processes such as nucleophilic addition, enolization, and condensation reactions, this ketone can be modified to introduce functional groups or form carbon-carbon bonds. These reactions enable the synthesis of key intermediates and complex molecules in the pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and material science industries.Furthermore, 2-methylpentan-3-one can participate in asymmetric synthesis as a chiral auxiliary or as part of a chiral ligand system. By leveraging the stereochemical properties of this ketone, chemists can access enantiomerically pure compounds with high selectivity. This aspect is crucial for the production of pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals with defined stereochemistry and biological activity.Overall, the diverse reactivity and applications of 2-methylpentan-3-one in chemical synthesis highlight its importance as a valuable tool for organic chemists seeking to design and construct complex molecules efficiently.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com