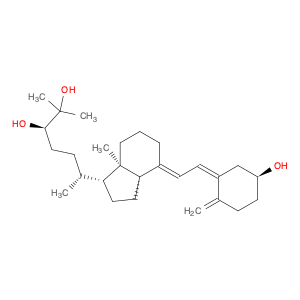
Secalciferol, also known as vitamin D2, plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis as a precursor for various pharmaceuticals and bioactive compounds. In the realm of organic chemistry, Secalciferol can be utilized as a starting material for the synthesis of different vitamin D analogs and derivatives. Its unique structure and functional groups make it a versatile building block for creating new drug candidates and compounds with potential therapeutic applications.In drug development, Secalciferol serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceutical agents that target conditions related to bone health, immune system modulation, and hormone regulation. By accessing the core structure of Secalciferol, chemists can modify its chemical properties to enhance bioavailability, stability, and specificity towards specific biological targets. This molecular manipulation allows for the design of more potent and selective drugs with improved pharmacokinetic profiles.Moreover, Secalciferol's role extends beyond traditional pharmaceutical synthesis to encompass the preparation of analytical standards and reference materials used in chemical testing and quality control processes. Its chemical reactivity and stability characteristics make it a preferred compound for formulating calibration solutions and verifying the accuracy of analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry.In summary, the strategic application of Secalciferol in chemical synthesis unlocks a myriad of possibilities for advancing drug discovery, material science, and analytical chemistry efforts. Its versatility and compatibility with various synthetic methodologies make it a valuable asset in the quest for developing innovative solutions for human health and scientific research.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com