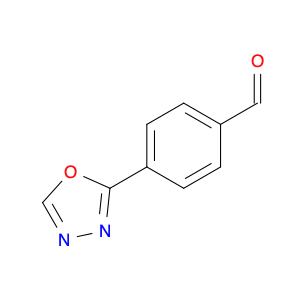
4-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzaldehyde, a versatile compound that finds its application in various chemical synthesis processes, acts as a key intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials. Its unique structure containing an oxadiazole ring and a benzaldehyde moiety imparts distinct reactivity and functional properties that make it a valuable building block in organic chemistry.In organic synthesis, 4-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzaldehyde serves as a precursor for the preparation of diverse heterocyclic compounds with potential biological activities. Its ability to undergo various chemical transformations such as nucleophilic addition, condensation reactions, and cyclization processes enables the synthesis of complex molecules with tailored properties. Moreover, the presence of the oxadiazole ring offers opportunities for designing new compounds with improved pharmacological profiles and enhanced performance in drug discovery and development.Additionally, this compound's role extends to the synthesis of functional materials and organic dyes due to its aromatic nature and electron-rich heterocyclic structure. By incorporating 4-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzaldehyde into the molecular structure of polymers or organic frameworks, researchers can modulate the material's properties such as optical, electronic, and thermal characteristics, thus enabling the development of advanced materials for various applications in electronics, optoelectronics, and sensing technologies.Overall, the significance of 4-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzaldehyde in chemical synthesis lies in its versatility as a starting material for constructing diverse molecular scaffolds and functional molecules that contribute to the advancement of pharmaceutical, agricultural, and material science sectors.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com