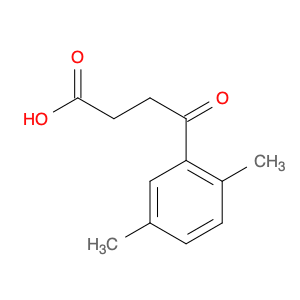
4-(2,5-Dimethylphenyl)-4-oxobutanoic acid, also known as $name$, serves as a versatile building block in chemical synthesis, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. Due to its unique structure and functional groups, this compound is commonly employed as a key intermediate in the production of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals.
$name$ is frequently utilized as a precursor in the synthesis of bioactive molecules such as pharmaceuticals and herbicides. Its chemical reactivity allows for the introduction of different functional groups through various chemical transformations, making it a valuable tool in the design and preparation of novel compounds with specific biological activities.
In addition, $name$ can participate in a range of organic reactions, including acylation, condensation, and cyclization processes, enabling the creation of structurally diverse molecules with potential applications across different industries. Its stability and compatibility with other reagents make it a preferred choice for synthetic chemists seeking to access complex molecular structures efficiently.
Moreover, the presence of the 2,5-dimethylphenyl moiety in $name$ imparts desirable properties to the synthesized compounds, such as enhanced stability, lipophilicity, and biological interactions. This feature further expands the potential applications of $name$ in drug discovery and development, as well as in the synthesis of functional materials with tailored properties.
Overall, the strategic incorporation of 4-(2,5-Dimethylphenyl)-4-oxobutanoic acid into chemical synthesis processes offers researchers a valuable tool for the creation of diverse chemical entities with potential applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com