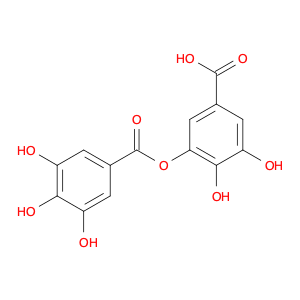
Digallic acid, also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid, is a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound found in various plants such as gallnuts, sumac, and some fruits. In chemical synthesis, digallic acid serves as a versatile building block for the production of advanced materials and pharmaceuticals. Its unique structure and reactivity make it a valuable precursor in the following applications:1. Metal Chelation: Digallic acid is known for its strong chelating properties due to the presence of multiple hydroxyl groups. It can effectively bind to metal ions like iron, copper, and zinc, forming stable complexes. This ability makes it suitable for metal extraction, wastewater treatment, and preparation of metal-based catalysts.2. Antioxidant Activity: The antioxidant properties of digallic acid make it a popular choice in the development of antioxidant supplements and cosmetics. Its ability to scavenge free radicals and prevent oxidative damage contributes to its anti-aging and protective effects on skin and hair.3. Tannin Production: Digallic acid is a key component in the synthesis of tannins, which are widely used in tanning leather, dyeing textiles, and manufacturing adhesive resins. Its presence enhances the tanning process by forming stable complexes with proteins in animal hides.4. Polymer Chemistry: Due to its ability to crosslink with proteins and other organic molecules, digallic acid finds applications in polymer chemistry. It is used in the synthesis of polymer networks, hydrogels, and bio-based materials with tailored properties for various industrial and biomedical applications.Overall, digallic acid's diverse applications in chemical synthesis highlight its significance as a multifunctional compound with potential for innovation in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and environmental technologies.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com