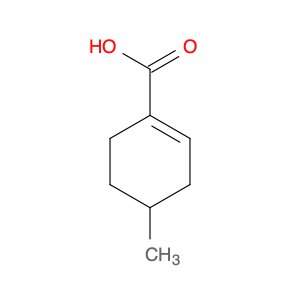
4-Methylcyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylic acid, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis processes. Its unique chemical structure makes it a valuable building block for the synthesis of various organic compounds. In particular, $name$ is commonly employed as a precursor in the production of pharmaceutical intermediates, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals due to its ability to undergo diverse chemical reactions.One of the key applications of 4-Methylcyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylic acid in chemical synthesis is its role as a starting material for the synthesis of substituted cyclohexanones. By reacting $name$ with different reagents and catalysts, chemists can introduce functional groups at specific positions on the cyclohexane ring, allowing for the creation of structurally diverse compounds that are essential in drug discovery and material science.Moreover, 4-Methylcyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylic acid can be utilized in the preparation of cyclic compounds through cyclization reactions. Its reactivity towards various nucleophiles and electrophiles enables the formation of complex ring structures with high selectivity and efficiency, making it a valuable tool for organic chemists seeking to access challenging molecular architectures.Additionally, $name$ can serve as a key intermediate in the synthesis of natural products and bioactive molecules. Its functional group compatibility and stereochemical properties make it an ideal starting material for the construction of complex molecular frameworks found in biologically active compounds, making it a crucial component in the development of new pharmaceutical agents and agrochemicals.Overall, the versatility and reactivity of 4-Methylcyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylic acid make it an indispensable tool in modern chemical synthesis, enabling the efficient construction of intricate organic molecules with diverse applications in the pharmaceutical, agricultural, and materials industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com