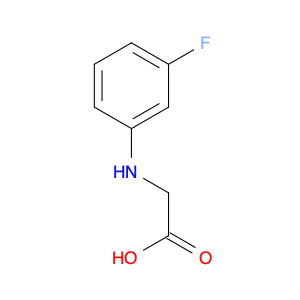
N-(3-Fluorophenyl)glycine is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis for its unique properties and applications. This amino acid derivative is often employed as a key building block in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its fluorine substitution provides enhanced reactivity and selectivity in various reactions, making it an essential component in organic synthesis strategies.
In peptide synthesis, N-(3-Fluorophenyl)glycine serves as a vital intermediate for incorporating fluorinated amino acids into peptide structures, imparting desired biological activities or structural modifications. Its presence can significantly influence the pharmacological properties of peptide-based drugs by improving stability, bioavailability, or binding affinity to target proteins.
Furthermore, in the development of medicinal compounds, this compound plays a crucial role in the modification of drug molecules to enhance their potency, selectivity, or metabolic stability. The incorporation of N-(3-Fluorophenyl)glycine moieties into drug candidates can lead to improved therapeutic profiles and reduced side effects, offering novel solutions for treating various diseases.
Overall, the application of N-(3-Fluorophenyl)glycine in chemical synthesis enables the design and synthesis of complex molecules with tailored properties, making it a valuable tool for researchers and chemists in drug discovery, materials science, and other fields requiring precision engineering of molecules and materials.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com