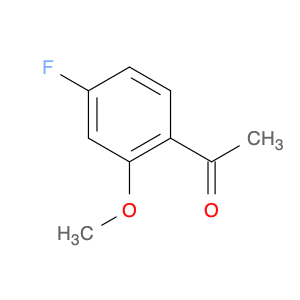
1-(4-Fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)ethanone, also known as $name$, is a versatile organic compound widely used in chemical synthesis as a key intermediate. Its unique structure allows for a diverse range of chemical reactions and transformations, making it an essential building block in the production of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials. In chemical synthesis, $name$ is commonly employed as a starting material for the synthesis of various biologically active compounds. Its functional groups enable it to participate in reactions such as nucleophilic substitution, Friedel-Crafts acylation, and Grignard reactions, facilitating the creation of complex molecular structures. By incorporating $name$ into the synthesis pathway, chemists can efficiently access a wide array of target molecules with specific properties and functionalities.Additionally, the presence of the fluoro and methoxy substituents in $name$ provides opportunities for tuning the reactivity and selectivity of the compound in chemical reactions. This control over reactivity is crucial in designing synthetic routes with high efficiency and precision, ultimately leading to the successful production of valuable compounds for various applications.Overall, the application of 1-(4-Fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)ethanone in chemical synthesis highlights its significance as a crucial intermediate in the preparation of diverse compounds with pharmaceutical, agricultural, and material science applications. Its versatility and unique structural features make it an indispensable tool for synthetic chemists seeking to develop innovative and efficient routes for the synthesis of complex molecules.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com