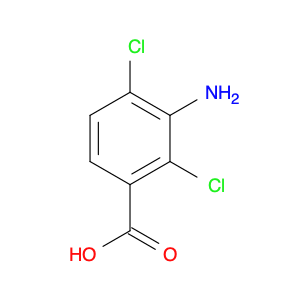
3-Amino-2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid is a versatile compound that finds important applications in chemical synthesis. In organic chemistry, this compound is commonly utilized as a building block or intermediate in the preparation of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes. Its unique structure, containing both an amino group and dichlorobenzoic acid moiety, makes it a valuable starting material for creating more complex molecules through synthetic pathways.One key application of 3-Amino-2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid is in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds, particularly in the formation of benzimidazole derivatives. By reacting this compound with appropriate reagents, chemists can access a wide range of benzimidazole structures that exhibit diverse biological activities. Benzimidazoles are important components in medicinal chemistry, serving as essential building blocks in the development of drugs targeting various diseases such as cancer, infections, and inflammatory conditions.Furthermore, 3-Amino-2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid can also serve as a valuable starting material for the synthesis of functionalized aromatic compounds. Through various transformations such as acylation, amidation, and coupling reactions, chemists can modify the amino and dichlorobenzoic acid groups to introduce different functional groups onto the benzene ring. These modifications can impart specific properties to the resulting molecules, making them suitable for use in materials science, organic electronics, and other advanced applications.Overall, the versatility of 3-Amino-2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid in chemical synthesis makes it a valuable tool for building complex molecular structures with tailored properties and functionalities. Its role in producing key intermediates for pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals highlights its importance in modern synthetic chemistry practices.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com