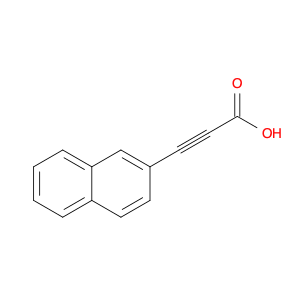
3-(Naphthalen-2-yl)propiolic acid, also known as Naphthylpropionic acid, is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis for various applications. As a functionalized propiolic acid derivative, this compound plays a crucial role in organic chemistry by serving as a key building block for the synthesis of diverse organic molecules.One of the primary applications of 3-(Naphthalen-2-yl)propiolic acid in chemical synthesis is its use as a precursor in the preparation of various functional materials. Through strategic derivatization and chemical transformation, this compound can be modified to introduce specific functional groups or structural motifs required for the synthesis of organic materials with desired properties. These materials find applications in fields such as materials science, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals.Furthermore, 3-(Naphthalen-2-yl)propiolic acid is utilized in the synthesis of biologically active compounds and pharmaceutical intermediates. By incorporating this building block into the molecular structure of target compounds, researchers can access a diverse range of bioactive molecules with potential therapeutic applications. The presence of the naphthalene moiety in the structure can also impart unique properties to the synthesized compounds, making them valuable candidates for further biological evaluation.Additionally, the reactivity of the propiolic acid functional group in 3-(Naphthalen-2-yl)propiolic acid enables its use in various carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions, such as cross-coupling and cycloaddition reactions. These synthetic transformations enable the efficient construction of complex molecular architectures, facilitating the rapid exploration of new chemical entities with potential industrial or academic importance.In summary, the application of 3-(Naphthalen-2-yl)propiolic acid in chemical synthesis spans a wide range of areas, including materials science, pharmaceuticals, and organic chemistry. Its versatility as a building block and its ability to participate in diverse synthetic transformations make it a valuable tool for researchers seeking to develop novel compounds with tailored properties and functionalities.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com